2023.07.10
M1チップでのlimaによるDocker環境構築
こんにちは、次世代システム研究室のT.Iです。
最近、仕事用のPCがM1のMacbookに変わったのですが、その際にDocker環境を構築しました。今回はその時の話をします。
1.Docker環境の仕組み
limaはMacOS上でlinuxの仮想環境を構築できるツールです。virtualboxやdocker desktopなどと同じ位置付けです。
今回のlimaを使用したdocker環境の仕組みは以下のようになっています。
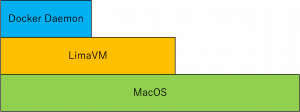
MacOS上にLimaでLinuxを立ち上げ、その中でDockerDaemonを起動します。実際に起動したContainerはLima上のLinuxとしてではなく、Limaで起動したLinuxの中のDocker Daemon上で動きます。
2.Limaの構築
limaは以下のようにhomebrewを使用してインストールできます。
$ brew install lima
limaでlinuxを起動する際は、yamlに設定を書きます。以下がM1でのDocker環境構築用のyamlです。
# Example to use Docker instead of containerd & nerdctl
# $ limactl start ./docker.yaml
# $ limactl shell docker docker run -it -v $HOME:$HOME --rm alpine
# To run `docker` on the host (assumes docker-cli is installed):
# $ export DOCKER_HOST=$(limactl list docker --format 'unix://{{.Dir}}/sock/docker.sock')
# $ docker ...
vmType: "vz"
rosetta:
enabled: true
binfmt: true
# This example requires Lima v0.8.0 or later
images:
- location: "https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/releases/22.04/release/ubuntu-22.04-server-cloudimg-arm64.img"
arch: "aarch64"
# CPUs: if you see performance issues, try limiting cpus to 1.
# ? Builtin default: 4
cpus: 8
# Memory size
# ? Builtin default: "4GiB"
memory: "24GiB"
# Disk size
# ? Builtin default: "100GiB"
disk: null
# Expose host directories to the guest, the mount point might be accessible from all UIDs in the guest
# ? Builtin default: null (Mount nothing)
# ? This file: Mount the home as read-only, /tmp/lima as writable
mounts:
- location: "~"
# Configure the mountPoint inside the guest.
# ? Builtin default: value of location
mountPoint: null
# CAUTION: `writable` SHOULD be false for the home directory.
# Setting `writable` to true is possible, but untested and dangerous.
# ? Builtin default: false
writable: null
- location: "/tmp/lima"
# ? Builtin default: false
# ? This file: true (only for "/tmp/lima")
writable: true
- location: "/path/to/mount_point/"
writable: true
# Mount type for above mounts, such as "reverse-sshfs" (from sshocker) or "9p" (EXPERIMENTAL, from QEMU’s virtio-9p-pci, aka virtfs)
# ? Builtin default: "reverse-sshfs"
mountType: "virtiofs"
containerd:
system: false
user: false
provision:
- mode: system
# This script defines the host.docker.internal hostname when hostResolver is disabled.
# It is also needed for lima 0.8.2 and earlier, which does not support hostResolver.hosts.
# Names defined in /etc/hosts inside the VM are not resolved inside containers when
# using the hostResolver; use hostResolver.hosts instead (requires lima 0.8.3 or later).
script: |
#!/bin/sh
sed -i 's/host.lima.internal.*/host.lima.internal host.docker.internal/' /etc/hosts
- mode: system
script: |
#!/bin/bash
set -eux -o pipefail
command -v docker >/dev/null 2>&1 && exit 0
export DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | sh
# NOTE: you may remove the lines below, if you prefer to use rootful docker, not rootless
systemctl disable --now docker
apt-get install -y uidmap dbus-user-session
- mode: user
script: |
#!/bin/bash
set -eux -o pipefail
systemctl --user start dbus
dockerd-rootless-setuptool.sh install
docker context use rootless
probes:
- script: |
#!/bin/bash
set -eux -o pipefail
if ! timeout 30s bash -c "until command -v docker >/dev/null 2>&1; do sleep 3; done"; then
echo >&2 "docker is not installed yet"
exit 1
fi
if ! timeout 30s bash -c "until pgrep rootlesskit; do sleep 3; done"; then
echo >&2 "rootlesskit (used by rootless docker) is not running"
exit 1
fi
hint: See "/var/log/cloud-init-output.log". in the guest
hostResolver:
# hostResolver.hosts requires lima 0.8.3 or later. Names defined here will also
# resolve inside containers, and not just inside the VM itself.
hosts:
host.docker.internal: host.lima.internal
portForwards:
- guestSocket: "/run/user/{{.UID}}/docker.sock"
hostSocket: "{{.Dir}}/sock/docker.sock"
message: |
To run `docker` on the host (assumes docker-cli is installed), run the following commands:
------
docker context create lima --docker "host=unix://{{.Dir}}/sock/docker.sock"
docker context use lima
docker run hello-world
------
ファイルの設定項目についてです。まず起動するlinuxについての設定です。
vmType: "vz" rosetta: enabled: true binfmt: true images: - location: "https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/releases/22.04/release/ubuntu-22.04-server-cloudimg-arm64.img" arch: "aarch64"
今回エミュレータはrosettaを使用します。m1Macのcpuアーキテクチャはarm64ですが、rosettaを使用することによってamd64のエミュレートが可能となります。他にもエミュレータはいくつかありますが、amd64のContainerを起動した際動かないアプリケーションがあったり、動作が遅かったりするものがあるためrosettaを使用します。
rosettaをlimaで使用する際は上記のように、vmのアーキテクチャはarm64である必要があります。また、MacOSを13以上にアップデートする必要があります。
※rosettaだと大体のamd64アプリケーションは動作しますが、たまに一部動かないものがあります。
limaVMが使用できるcpu、メモリ、diskは以下の項目で設定できます。
# CPUs: if you see performance issues, try limiting cpus to 1. # ? Builtin default: 4 cpus: 8 # Memory size # ? Builtin default: "4GiB" memory: "24GiB" # Disk size # ? Builtin default: "100GiB" disk: null
MacOSへのマウントについては以下で設定できます。
# Expose host directories to the guest, the mount point might be accessible from all UIDs in the guest # ? Builtin default: null (Mount nothing) # ? This file: Mount the home as read-only, /tmp/lima as writable mounts: - location: "~" # Configure the mountPoint inside the guest. # ? Builtin default: value of location mountPoint: null # CAUTION: `writable` SHOULD be false for the home directory. # Setting `writable` to true is possible, but untested and dangerous. # ? Builtin default: false writable: null - location: "/tmp/lima" # ? Builtin default: false # ? This file: true (only for "/tmp/lima") writable: true - location: "/path/to/mount_point/" writable: true # Mount type for above mounts, such as "reverse-sshfs" (from sshocker) or "9p" (EXPERIMENTAL, from QEMU’s virtio-9p-pci, aka virtfs) # ? Builtin default: "reverse-sshfs" mountType: "virtiofs"
注意点としては、limaでrosettaを使用する際にmountTypeはvirtiofsである必要があるということです。
最後にこちらはlimaVMが起動した際にDocker Daemonが立ち上がるようにする設定です。デフォルトだとnertctlが立ち上がります。
containerd:
system: false
user: false
provision:
- mode: system
# This script defines the host.docker.internal hostname when hostResolver is disabled.
# It is also needed for lima 0.8.2 and earlier, which does not support hostResolver.hosts.
# Names defined in /etc/hosts inside the VM are not resolved inside containers when
# using the hostResolver; use hostResolver.hosts instead (requires lima 0.8.3 or later).
script: |
#!/bin/sh
sed -i 's/host.lima.internal.*/host.lima.internal host.docker.internal/' /etc/hosts
- mode: system
script: |
#!/bin/bash
set -eux -o pipefail
command -v docker >/dev/null 2>&1 && exit 0
export DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | sh
# NOTE: you may remove the lines below, if you prefer to use rootful docker, not rootless
systemctl disable --now docker
apt-get install -y uidmap dbus-user-session
- mode: user
script: |
#!/bin/bash
set -eux -o pipefail
systemctl --user start dbus
dockerd-rootless-setuptool.sh install
docker context use rootless
probes:
- script: |
#!/bin/bash
set -eux -o pipefail
if ! timeout 30s bash -c "until command -v docker >/dev/null 2>&1; do sleep 3; done"; then
echo >&2 "docker is not installed yet"
exit 1
fi
if ! timeout 30s bash -c "until pgrep rootlesskit; do sleep 3; done"; then
echo >&2 "rootlesskit (used by rootless docker) is not running"
exit 1
fi
hint: See "/var/log/cloud-init-output.log". in the guest
hostResolver:
# hostResolver.hosts requires lima 0.8.3 or later. Names defined here will also
# resolve inside containers, and not just inside the VM itself.
hosts:
host.docker.internal: host.lima.internal
portForwards:
- guestSocket: "/run/user/{{.UID}}/docker.sock"
hostSocket: "{{.Dir}}/sock/docker.sock"
message: |
To run `docker` on the host (assumes docker-cli is installed), run the following commands:
------
docker context create lima --docker "host=unix://{{.Dir}}/sock/docker.sock"
docker context use lima
docker run hello-world
------
3.Dockerのインストール
MacOS上のターミナルからlimaVM上のDocker Daemonを操作するために、homebrewでdockerをインストールします。linux上のdocker Daemonを操作するため、もちろんdocker-composeも使用可能です。こちらも一緒にインストールします。
$ brew install docker docker-compose
4.LimaVmの起動
dockerのインストールが終わったら以下でlimaVMを起動します。
$ limactl start --name {VMName} {yaml}
{VMName}にはlimaで起動するlinuxの名前を入れます。また、{yaml}には最初に記載したlimaVMの設定をするためのyamlのパスを入れます。
次に、以下のコマンドを打ちます。limaVM内のdocker daemonとはsocketで通信するため、以下のコマンドでMacOS側のdockerクライアントにソケットの設定をします。
$ docker context create lima --docker "host=unix://{{.Dir}}/sock/docker.sock"
ここまで行えば、以下のように普通にDockerが使用できるようになるはずです。
$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
起動しているlimaVMを表示する際は以下でできます。
$ limactl list NAME STATUS SSH ARCH CPUS MEMORY DISK DIR default Running 127.0.0.1:60022 aarch64 8 16GiB 100GiB ~/.lima/default
こちらでlimaVMのターミナルにログインできます。
$ limactl shell {name}
limaVMを停止する際は以下のコマンドでできます。
$ limactl stop {name}
削除はこちらでできます。
$ limactl delete {name}
{name}は起動しているlimaVMの名前です。
最後に
次世代システム研究室では、グループ全体のインテグレーションを支援してくれるアーキテクトを募集しています。インフラ設計、構築経験者の方、次世代システム研究室にご興味を持って頂ける方がいらっしゃいましたら、ぜひ募集職種一覧からご応募をお願いします。 皆さんのご応募をお待ちしています
グループ研究開発本部の最新情報をTwitterで配信中です。ぜひフォローください。
Follow @GMO_RD