2021.01.12
UX向上の取組の最前線 – イーサリアムでのガスレストランザクションとオートメーション(後編)
(前編に続きます)
前編にガスレストランザクション周りのイーサリアム界隈での取組を紹介しましたが、如何でしょうか。
この記事でスマートコントラクトとのやり取りの複雑さを改善するためのGelatoと言うトランザクションのオートメーション(自動化)のGelatoプロジェクトを紹介したいです。
イーサリアムでのDeFiとやりとりするためにはトランザクションを出さないといけないですが、毎回ウォレットを開いてトランザクションを署名させて、イーサリアムにブロードキャストするのは面倒臭いではないでしょうか。
PASMOのオートチャージ、クレジットカードの自動引き落とし、アービトラージのボットのような自動化機能がイーサリアムのDeFiで実現できれば、一般な方々にもDeFiを簡単に触れますね。
今はGelatoはv1のbeta版ですが、v2の開発も進んでいるということです。
GelatoはPermissionlessかつNon-custodialのプロトコルとして、一体、トランザクションのオートメーション(自動化)はどのように実現できるのか。
さて、覗いてみましょう。
目次
4.オートメーションプロトコル – Gelato?
GelatoはEthereumでのスマートコントラクトの実行を自動化させるプロトコルです。IFTTT(If This, Then That)のボットのインフラと見做しても良いです。
スマートコントラクトは「自律的に実行できるスクリプト」と表現されることは多くですが、こちらの自律はほど遠いでしょう。
実際、スマートコントラクトはかなり怠惰です。 特定のロジックを実行するには、毎回EOAでトランザクションを作成する必要があります。
前編も紹介しましたが、開発者あるいはサービスプロバイダーがユーザーに代わってトランザクションを実行するが可能ですが、単一障害点(single point of failure、SPOF)の問題、あるいは特定な機能に限られている問題が抱えています。
ユーザーは複数のタスクを事前にイーサリアムに預けて(一つのトランザクションで済ませる)、タスクでのトランザクションの実行をGelatoにアウトソーシングで、想定のスケジュールの通りに済ませます。Gelatoは信頼できる万能のボットとなれるかと思います。
GelatoをDAPPプロジェクトに統合することで、リレーノードインフラストラクチャをわざわざ構築すること、または単一障害点となり得るリレーノードインフラストラクチャに信頼することがなくなります。
Gelato Executor Networkは、イーサリアムネットワークでの新しいタスクをリッスンする常時稼働の複数のボットで構成されています。 タスクの内、条件に満たして、実行可能になるタスクを分散型のボットのネットワークがユーザーに代わってタスクでのトランザクションを実行します。
トランザクションの実行の報酬(ガス代金+実行手数料)を獲得するために、誰でもExecutorノードを立て、ボットのネットワークに参加して、Gelato Executor Networkの堅牢性に貢献できます。
4−1.Gelatoのユースケース
以下のユースケースが想定られています。
- 定期的にトランザクションの実行。(例えば、10分毎にあるアドレスにトークン送金する、またはSwap 100 DAI to ETH on Uniswap every week)
- トークンのオートチャージ。(例えば、あるアカウントのトークンの残高が閾値以下になる場合、このアカウント宛てに閾値までトークンをチェージする)
- DEXでのアービトラージ。(例えば、USDTーDAI取引ペアーで、1USDT >= 1.2DAIの時、USDTでDAIを購入する)
- 異なるレンディングプロトコルでのイールドファーミング(Yield Farming)の自動執行
あなたの豊富な想像力に任せば、Gelatoを活かせて、DeFiがより綺麗に彩られるかと思います。
4-2.Gelatoネットワーク
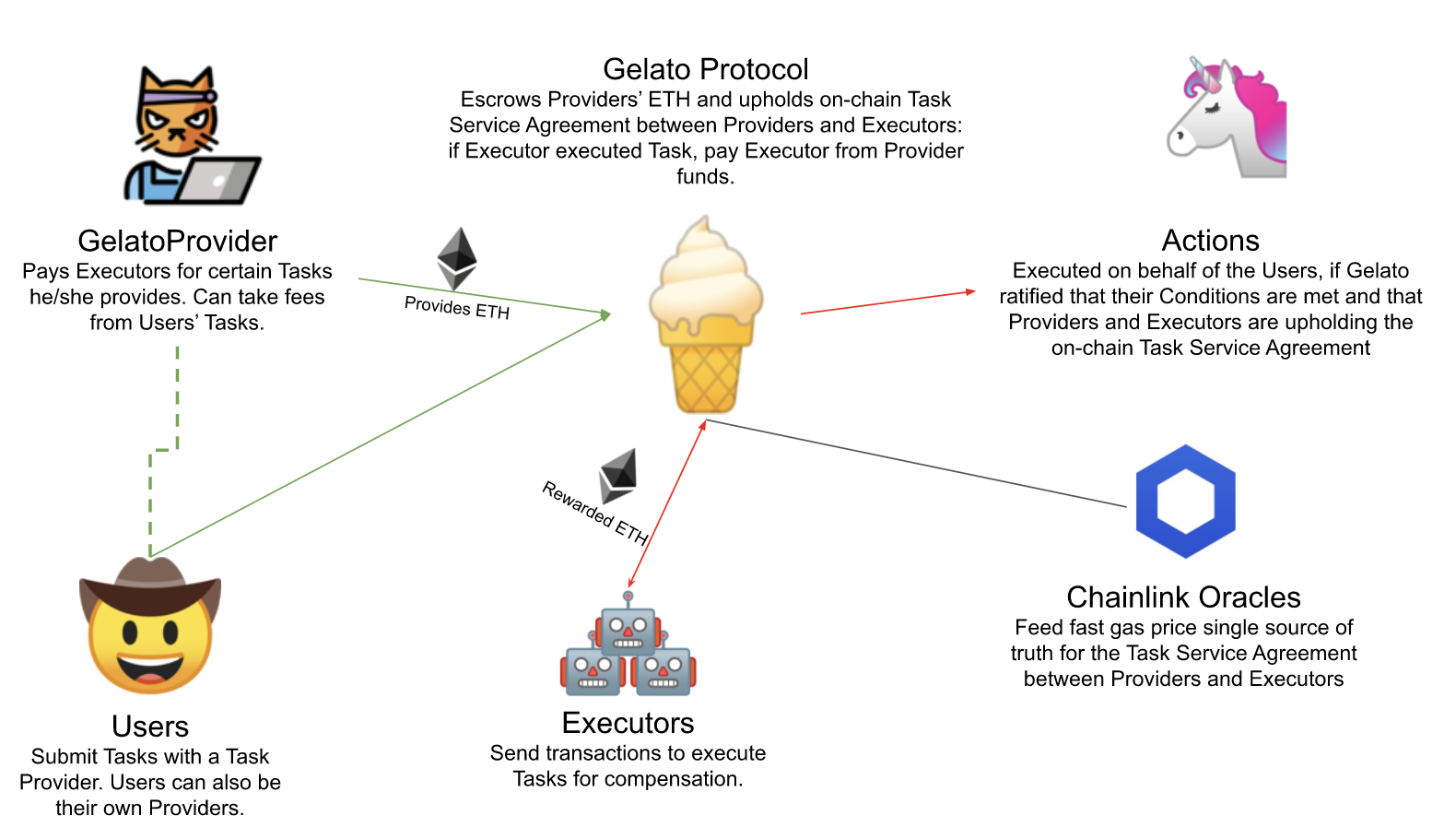
出典:https://github.com/gelatodigital/gelato-network
Gelato Protocol
Gelato ProviderのETHを預託し、ProviderとExecutor間のオンチェーンサービス契約の執行を守ります。即ち、
Executorがタスクでのトランザクションが成功に実行された場合は、Providerのデポジットからガス代金+手数料をExecutorに支払うことです。
ロジックはGelatoコアコントラクトにまとめられています。
contract GelatoCore {
// Gelato Providerのガスタンク
mapping(address => uint256) public override providerFunds;
// Gelato ProviderのETHを預託する
function provideFunds(address _provider) public payable override {
require(msg.value > 0, "GelatoProviders.provideFunds: zero value");
uint256 newProviderFunds = providerFunds[_provider].add(msg.value);
emit LogFundsProvided(_provider, msg.value, newProviderFunds);
providerFunds[_provider] = newProviderFunds;
}
// Executorがタスクを実行する
function exec(TaskReceipt memory _TR) external override {
try this.executionWrapper{
gas: gasleft().sub(internalGasRequirement, "GelatoCore.exec: Insufficient gas")
}(_TR, gasLimit, gelatoGasPrice)
returns (ExecutionResult _executionResult, string memory _reason)
{
executionResult = _executionResult;
reason = _reason;
}
// 実行成功する場合
if (executionResult == ExecutionResult.ExecSuccess) {
// Providerのデポジットからガス代金+手数料を差し引く
executorCompensation = executorSuccessFee(cappedGasUsed, _gelatoGasPrice);
sysAdminCompensation = sysAdminSuccessFee(cappedGasUsed, _gelatoGasPrice);
providerFunds[_provider] = providerFunds[_provider].sub(
executorCompensation.add(sysAdminCompensation),
"GelatoCore._processProviderPayables: providerFunds underflow"
);
// ガス代金+手数料ををExecutorに支払う
executorStake[msg.sender] += executorCompensation;
}
}
}
GelatoProviders
GelatoコアコントラクトにETHをデポジットするEOAアカウントです。
デポジットのETHはGelatoガスタンクとして、トランザクション実行のガス代金が差し引かれて、実行者のExecutorsへ送られます。
2つ種類のGelato Providerがあります。
- External-Providers – Dappユーザーに代わってExecutorにガスを支払います。 これで、DappユーザーはETHをデポジットする必要をなくすことで、ユーザーに優れたUXを提供できる。
- Self-Providers – DappユーザーはExecutorに直接にガスを支払う。したがって、ETHをデポジットする必要があります。
そして、いつでもデポジットのETHをEOAアカウントに引き戻せます。
// Unprovide funds
function unprovideFunds(uint256 _withdrawAmount)
public
override
returns(uint256 realWithdrawAmount)
{
uint256 previousProviderFunds = providerFunds[msg.sender];
realWithdrawAmount = Math.min(_withdrawAmount, previousProviderFunds);
uint256 newProviderFunds = previousProviderFunds - realWithdrawAmount;
// Effects
providerFunds[msg.sender] = newProviderFunds;
// Interaction
msg.sender.sendValue(realWithdrawAmount);
emit LogFundsUnprovided(msg.sender, realWithdrawAmount, newProviderFunds);
}
Users
将来実行したいトランザクションをタスクに埋めて、ガス代金を支払うGelatoProviderを指定して、タスクをGelato Executor NetworkにサブミットするDappユーザーです。
ユーザーの秘密鍵にアクセスせずに、第三者の誰でもユーザーに代わってトランザクションを送信するにはどうすればよいですか?
Gelatoはウォレットコントラクトを採用しました。ウォレットコントラクトについて、前編で紹介したこともあります。
ユーザー毎にウォレットコントラクトをデプロイし、ユーザーのプロキシとして、Gelatoプロトコルと対話する仕組みとなります。
よく使われるウォレットコントラクトのGnosis SafeやDsProxyはもちろん、自作のプロキシコントラクトまたはGelato開発したGelatoUserProxyもGelatoプロトコルに向いています。
ユーザーはGelatoUserProxyFactoryコントラクト通して、ユーザーと紐付けるGelatoUserProxyをデプロイします。
contract GelatoUserProxyFactory is IGelatoUserProxyFactory {
// create2でGelatoUserProxyをデプロイする
function createTwo(uint256 _saltNonce)
public
payable
override
returns (GelatoUserProxy userProxy)
{
bytes32 salt = keccak256(abi.encode(msg.sender, _saltNonce));
userProxy = new GelatoUserProxy{salt: salt, value: msg.value}(msg.sender, gelatoCore);
require(
address(userProxy) == predictProxyAddress(msg.sender, _saltNonce),
"GelatoUserProxyFactory.createTwo: wrong address prediction"
);
}
// create2でGelatoUserProxyをデプロイしてから、アクションを実行する
function createTwoExecActions(uint256 _saltNonce, Action[] calldata _actions)
external
payable
override
returns (GelatoUserProxy userProxy)
{
userProxy = createTwo(_saltNonce);
if (_actions.length != 0) userProxy.multiExecActions(_actions)
}
}
GelatoUserProxyをアクセスできるのはユーザーのEOAアカウント以外には、gelatoCoreとGelatoUserProxyFactoryも加えました。これで、第三者のExecutorはgelatoCore通して、トランザクションの実行が可能となります。
contract GelatoUserProxy is IGelatoUserProxy {
constructor(address _user, address _gelatoCore)
public
payable
noZeroAddress(_user)
noZeroAddress(_gelatoCore)
{
factory = msg.sender;
user = _user;
gelatoCore = _gelatoCore;
}
modifier auth() {
require(
msg.sender == gelatoCore || msg.sender == user || msg.sender == factory,
"GelatoUserProxy.auth: failed"
);
_;
}
function multiExecActions(Action[] calldata _actions) public payable override auth {
for (uint i = 0; i < _actions.length; i++) {
if (_actions[i].operation == Operation.Call)
_callAction(_actions[i].addr, _actions[i].data, _actions[i].value);
else if (_actions[i].operation == Operation.Delegatecall)
_delegatecallAction(address(_actions[i].addr), _actions[i].data);
else
revert("GelatoUserProxy.multiExecActions: invalid operation");
}
}
}
Executors
イーサリアムネットワークでの新しいタスクを常にリッスンし、条件に満たして実行可能になるタスクをユーザーに代わってタスクでのトランザクションを実行するボットはExecutorです。複数のExecutorでGelato Executor Networkが構成されます。
少額の手数料(最初は、正常に実行された各タスクの総ガスコストの2%であり、ユーザー/ GelatoProviderがGelatoでデポジットの残高から支払われる)を受け取ることで、Executorの構築が促されます。
テストネットに繋がってサービスの提供しているExecutorボット群は、Gelato チームにより管理されて、常に稼働していて複数のノードで構成されたインフラストラクチャです。 1つのボットがダウンしている場合でも、他の複数がアップしていますので、サービス停止の心配がありません。
このスマートコントラクト通して、タスク処理を行います。
contract PermissionedExecutors {
address public constant first_executor = 0x4d671CD743027fB5Af1b2D2a3ccbafA97b5B1B80;
address public constant second_executor = 0x99E69499973484a96639f4Fb17893BC96000b3b8;
modifier onlyExecutors {
require(
msg.sender == first_executor || msg.sender == second_executor,
"PermissionedExecutors.onlyExecutor"
);
_;
}
/// @notice only the hardcoded Executors can call this
/// @dev Caution: there is no built-in coordination mechanism between the 2
/// Executors. Only one Executor should be live at all times, lest they
/// will incur tx collision costs.
function exec(TaskReceipt calldata _TR) public virtual onlyExecutors {
try IGelatoCore(gelatoCore).exec(_TR) {
} catch Error(string memory error) {
error.revertWithInfo("PermissionedExecutors.exec:");
} catch {
revert("PermissionedExecutors.exec:unknown error");
}
}
}
Chainlink Oracles
GelatoはChainlinkオラクルを使用して、Executorsが使用できるGasPriceを規制し、公正な市場レートを確保します。
Task (Conditions + Actions)
ユーザーは、デプロイされたウォレットコントラクトを介してGelatoにタスクを送信します。
タスクはConditions (when to execute a transaction、実行条件) と Actions (what the transaction should execute、実行アクション)で構成されます。
・ Conditions
ConditionsはGelatoCoreスマートコントラクトによってチェックされるスマートコントラクトであり、特定のブロックでタスクを実行できるかどうかを決定します。
使うには、GelatoConditionsStandardを継承して、ok関数を実装する必要があります。
/// @title IGelatoCondition - solidity interface of GelatoConditionsStandard
/// @notice all the APIs of GelatoConditionsStandard
/// @dev all the APIs are implemented inside GelatoConditionsStandard
interface IGelatoCondition {
/// @notice GelatoCore calls this to verify securely the specified Condition securely
/// @dev Be careful only to encode a Task's condition.data as is and not with the
/// "ok" selector or _taskReceiptId, since those two things are handled by GelatoCore.
/// @param _taskReceiptId This is passed by GelatoCore so we can rely on it as a secure
/// source of Task identification.
/// @param _conditionData This is the Condition.data field developers must encode their
/// Condition's specific parameters in.
/// @param _cycleId For Tasks that are executed as part of a cycle.
function ok(uint256 _taskReceiptId, bytes calldata _conditionData, uint256 _cycleId)
external
view
returns(string memory);
}
abstract contract GelatoConditionsStandard is IGelatoCondition {
string internal constant OK = "OK";
}
Conditionの定義は以下のようです。
struct Condition {
IGelatoCondition inst; // instは事前にデプロイしたConditionコントラクトのアドレス
bytes data; // Conditionコントラクトの方法とパラメーターのペイロードデータ
}
Galatoは既に多くのConditionのテンプレートを提供していたので、githubで参照できます。
一番理解しやすいConditionTimeStatefulで説明してみます。
function ok(uint256 _taskReceiptId, bytes calldata _conditionData, uint256)
public
view
virtual
override
returns(string memory)
{
// 条件を満たすかcheckRefTime方法より判断する
address userProxy = abi.decode(_conditionData[36:], (address));
return checkRefTime(_taskReceiptId, userProxy);
}
/// @dev Abi encode these parameter inputs. Use a placeholder for _taskReceiptId.
/// @param _taskReceiptId Will be stripped from encoded data and replaced by
/// the value passed in from GelatoCore.
function checkRefTime(uint256 _taskReceiptId, address _userProxy)
public
view
virtual
returns(string memory)
{
// Conditionで事前に設定した時間_refTimeは現在のブロックタイムblock.timestampの前の場合、条件を満たしたことと見なす
uint256 _refTime = refTime[_userProxy][_taskReceiptId];
if (_refTime <= block.timestamp) return OK;
return "NotOkTimestampDidNotPass";
}
ExecutorはgelatoCore通して、トランザクションの実行をする前には、Conditionのok方法を呼び出して事前に定義した条件を満たしているかどうかチェックします。
function canExec(TaskReceipt memory _TR, uint256 _gasLimit, uint256 _gelatoGasPrice)
public
view
override
returns(string memory)
{
// Optional CHECK Condition for user proxies
if (_TR.task().conditions.length != 0) {
for (uint i; i < _TR.task().conditions.length; i++) {
// Conditionのok方法を呼び出す
try _TR.task().conditions[i].inst.ok(
_TR.id,
_TR.task().conditions[i].data,
_TR.cycleId
)
returns(string memory condition)
{
// OKを返却できれば、条件に満たしたことと見なす
if (!condition.startsWithOK())
return string(abi.encodePacked("ConditionNotOk:", condition));
} catch Error(string memory error) {
return string(abi.encodePacked("ConditionReverted:", error));
} catch {
return "ConditionReverted:undefined";
}
}
}
}
・ Actions
ActionsはユーザーのウォレットコントラクトのGelatoUserProxyによってチェックまたは実行のロジックを含むスマートコントラクトです。
Actionの定義は以下の通りです。
// Operationが2つ種類があります。
enum Operation { Call, Delegatecall }
enum DataFlow { None, In, Out, InAndOut }
struct Action {
address addr; // スマートコントラクトのアドレス
bytes data; // 呼び出すスマートコントラクトの方法のペイロード
Operation operation; // call or delegatecall
DataFlow dataFlow; // 複数のアクション間でデータの流れであり、インプットのパラメーターまたは実行結果のアウトプット
uint256 value; // ETH(ETH送金しない場合、0にする)
bool termsOkCheck; // スマートコントラクトを実行する前に、ペイロードの中身をチェックするか
}
Call, Delegatecallについて、以下の図は良くまとめたと思います。
コンテキストのmsg.sender、msg.valueが異なります。
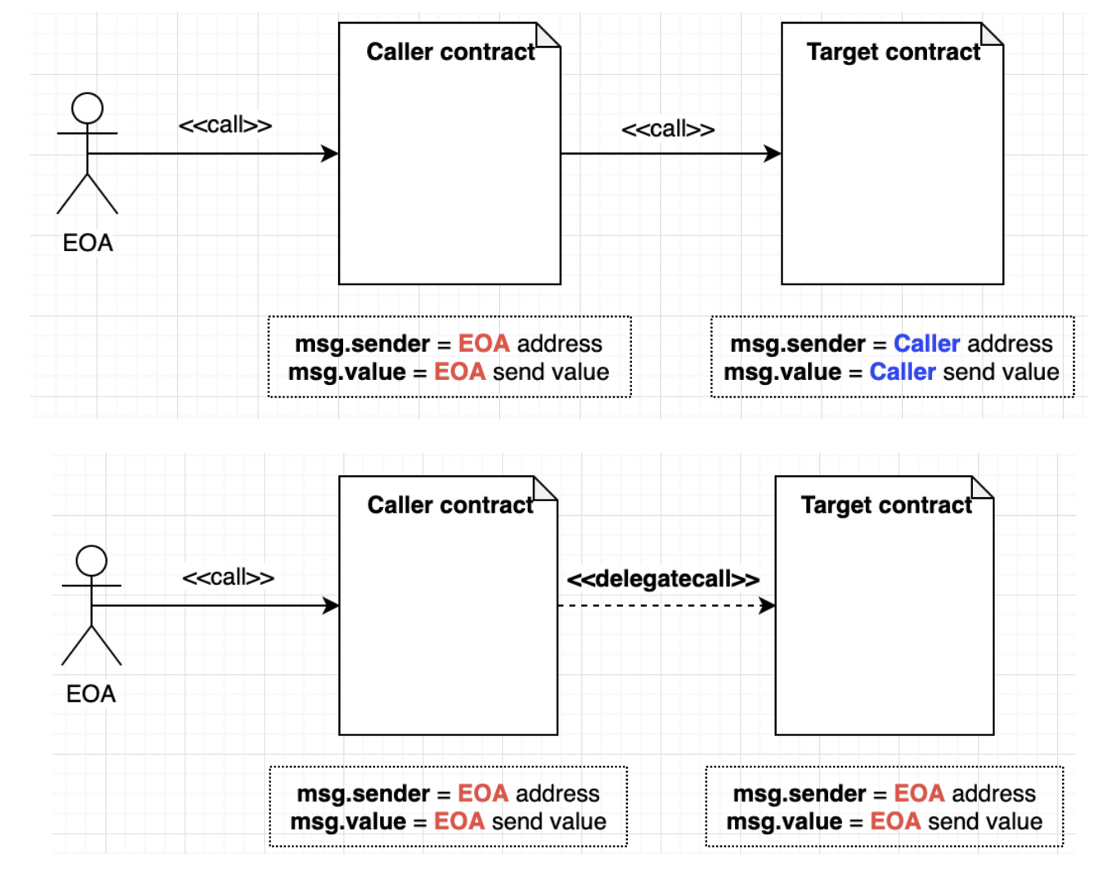
出典:https://medium.com/coinmonks/delegatecall-calling-another-contract-function-in-solidity-b579f804178c
Galatoは既に多くのActionのテンプレートを提供していたので、githubで参照できます。
一番理解しやすいActionTransferで説明していみます。
contract ActionTransfer {
... ...
// トークンまたはETHをcallerからdestination送金するアクション(delegatecallOnly、delegatecallに限られている)
function action(address sendToken, uint256 sendAmount, address destination)
public
virtual
delegatecallOnly("ActionTransfer.action")
{
if (sendToken != ETH_ADDRESS) {
IERC20 sendERC20 = IERC20(sendToken);
sendERC20.safeTransfer(destination, sendAmount, "ActionTransfer.action:");
emit LogOneWay(address(this), sendToken, sendAmount, destination);
} else {
payable(destination).sendValue(sendAmount);
}
}
// callerの残高は送金の金額にカバーできるかどうかチェックする
function termsOk(
uint256, // taskReceipId
address _userProxy,
bytes calldata _actionData,
DataFlow _dataFlow,
uint256, // value
uint256 // cycleId
)
public
view
virtual
override
returns(string memory)
{
... ...
// ターゲットトークンアドレスと送金金額を取得する
(address sendToken, uint256 sendAmount) = abi.decode(
_actionData[4:68],
(address,uint256)
);
if (sendToken == ETH_ADDRESS) {
if (_userProxy.balance < sendAmount)
return "ActionTransfer: NotOkUserProxyETHBalance";
} else {
try IERC20(sendToken).balanceOf(_userProxy) returns(uint256 sendTokenBalance) {
if (sendTokenBalance < sendAmount)
return "ActionTransfer: NotOkUserProxyERC20Balance";
} catch {
return "ActionTransfer: ErrorBalanceOf";
}
}
// STANDARD return string to signal actionConditions Ok
return OK;
}
// delegatecallOnlyの実現は巧妙ですね。callerはこのアクションをdelegatecallする場合だけ、thisはcallerのアドレスとなり、
// constructorでのthisのアクションのアドレスと異なります。
constructor() public { thisActionAddress = address(this); }
address public immutable thisActionAddress;
modifier delegatecallOnly(string memory _tracingInfo) {
require(
thisActionAddress != address(this),
string(abi.encodePacked(_tracingInfo, ":delegatecallOnly"))
);
_;
}
... ...
}
・ タスクの実行のオートメーション
ユーザーのタスクは事前に設定したスケジュール通りに繰り返しに実行されます。タスクの出す(submitTaskCycle)トランザクションにはユーザーのガス(ETH)がかかりますが、タスクでの将来のアクションの実行については自分の負担するか(Self-Provider)または第三者に肩代わりに負担するか(External-Provider)選択することとなります。
ユーザーはタスクを出す時、実行のサイクル数(cycles)を指定します。
function submitTaskCycle(
Provider calldata _provider,
Task[] calldata _tasks,
uint256 _expiryDate,
uint256 _cycles // num of full cycles
)
public
override
userOrFactory
{
try IGelatoCore(gelatoCore).submitTaskCycle(
_provider,
_tasks,
_expiryDate,
_cycles
) {
} catch Error(string memory err) {
revert(string(abi.encodePacked("GelatoUserProxy.submitTaskCycle:", err)));
} catch {
revert("GelatoUserProxy.submitTaskCycle:undefinded");
}
}
ExecutorはConditionに満たして、実行可能なタスクを実行して、成功となる場合はこのサイクル数(cycles)によって、再度タスクを実行キューに保存しといて、次のサイクルを待たせます。
unction _exec(TaskReceipt memory _TR) private {
... ...
// Execution via UserProxy
(bool success, bytes memory userProxyReturndata) = _TR.userProxy.call(execPayload);
// SUCCESS
if (success) {
// Optional: Automated Cyclic Task Submissions
if (_TR.submissionsLeft != 1) {
_storeTaskReceipt(
false, // newCycle?
_TR.userProxy,
_TR.provider,
_TR.nextIndex(),
_TR.tasks,
_TR.expiryDate,
_TR.cycleId,
_TR.submissionsLeft == 0 ? 0 : _TR.submissionsLeft - 1
);
}
}
... ...
}
ちなみに、実行のサイクル数(cycles)を0にする場合は、無限実行させることとなります。
4-3.Gelatoのアクセス管理
Dapp開発者またはDappサービスプロバイダーはExternal-Providersとして、Dappユーザーに代わってExecutorにガスを支払うことで、DappユーザーはETHをデポジットする必要をなくすことで、ユーザーに優れたUXを提供できます。External-Providersもガス支払代行のビジネスモデルを構築することで、利益を獲得する可能性があります。
gelatoは、ProviderModulesスマートコントラクトでユーザーのアクセス管理(誰かがExternal-Providersのガス支払代行サービス利用できる)、TaskSpecsでユーザーのタスクの許可管理(タスクの悪用防止できる)、事前にExecutorコントラクトのアドレスの指定(providerAssignsExecutor)でExecutorのアクセスの管理を行います。
ProviderModules
Gelatoプロトコルとやり取りするのがプロキシスマートコントラクトである必要があります。
どのようなタイプのプロキシの利用可能かのロジックはProviderModuleに実装されています。
ProviderModuleはホワイトリストで、ACL管理も行えます。
ProviderModuleを自作する場合、GelatoProviderModuleStandardを継承することとなります。
Galatoは既に多くのProviderModuleのテンプレートを提供していたので、githubで参照できます。
abstract contract GelatoProviderModuleStandard {
string internal constant OK = "OK";
function isProvided(address, address, Task calldata)
external
view
virtual
override
returns(string memory)
{
// ここでホワイトリストを設ける。許可のあるプロキシのみOKを返却する。
return OK;
}
... ...
}
TaskSpecs
GelatoのExternal-Providersがユーザーのトランザクションのガス料金を支払うことで、ユーザーは勝手にこれを悪用して、Providersにすべてのトランザクションのガス料金を支払わせ、恣意的にタダのイーサリアムUXを楽しむことができないのではないかと思いがちですね。
External-Providersは事前にガス料金を支払おうとするタスク種類をTaskSpecというホワイトリストに登録することでユーザーの実行可能なタスクを制約します。
javascriptでのTaskSpecの定義
const action1 = new Action({
addr: actionAddress,
// no need to include action.data for Task Specs
operation: Operation.Delegatecall, // We are using an action Script here, see smart contract: ActionERC20TransferFrom.sol
dataFlow: DataFlow.None, // Only relevant if this action should return some value to the next, which it not necessary here
termsOkCheck: true, // After the condition is checked, we will also conduct checks on the action contract
value: 0, // Actions that use delegatecall always have value = 0
data: constants.HashZero, // Task Specs dont need data
});
// ##### Action #2
const action2 = new Action({
addr: conditionAddress, // We use the condition as an action (to dynamically set the timestamp when the users proxy contract can execute the actions next time)
// no need to include action.data for Task Specs
operation: Operation.Call, // We are calling the contract instance directly, without script
dataFlow: DataFlow.None, // Only relevant if this action should return some value to the next, which it not necessary here
termsOkCheck: false, // This action does not need a termsOk check
value: 0, // Actions that use delegatecall always have value = 0
data: constants.HashZero, // Task Specs dont need data
});
// ##### Create Task Spec
const taskSpec = new TaskSpec({
conditions: [condition.inst], // only need the condition inst address here
actions: [action1, action2], // Actions will be executed from left to right after each other. If one fails, all fail
gasPriceCeil: 0, // Here providers can set the maximum gas price they are willing to pay. Set to 0 to allow any gas price
});
gelatoCoreコントラクトで、provideTaskSpecsでTaskSpecを登録する。
contract GelatoCore {
... ...
// External-Providersにより、複数のTaskSpecを登録するが可能です。
function provideTaskSpecs(TaskSpec[] memory _taskSpecs) public override {
for (uint i; i < _taskSpecs.length; i++) {
if (_taskSpecs[i].gasPriceCeil == 0) _taskSpecs[i].gasPriceCeil = NO_CEIL;
bytes32 taskSpecHash = hashTaskSpec(_taskSpecs[i]);
setTaskSpecGasPriceCeil(taskSpecHash, _taskSpecs[i].gasPriceCeil);
}
}
function setTaskSpecGasPriceCeil(bytes32 _taskSpecHash, uint256 _gasPriceCeil)
public
override
{
uint256 currentTaskSpecGasPriceCeil = taskSpecGasPriceCeil[msg.sender][_taskSpecHash];
require(
currentTaskSpecGasPriceCeil != _gasPriceCeil,
"GelatoProviders.setTaskSpecGasPriceCeil: Already whitelisted with gasPriceCeil"
);
// ホワイトリストに追加する
taskSpecGasPriceCeil[msg.sender][_taskSpecHash] = _gasPriceCeil;
}
... ...
}
Executorへのアクセス
ProvidersはExecutorコントラクトの指定で、ユーザーのタスクの実行をこのExecutorに任せます。
contract GelatoCore {
... ...
mapping(address => uint256) public override executorProvidersCount;
// Called by Providers
function providerAssignsExecutor(address _newExecutor) public override {
address currentExecutor = executorByProvider[msg.sender];
require(
currentExecutor != _newExecutor,
"GelatoProviders.providerAssignsExecutor: already assigned."
);
if (_newExecutor != address(0)) {
require(
// ほら、Executorになるためには、ETHをgelatoにステーキングする必要があるよ。
// これで、Executorの不作為、不正に罰則を課す。
isExecutorMinStaked(_newExecutor),
"GelatoProviders.providerAssignsExecutor: isExecutorMinStaked()"
);
}
// EFFECTS: Provider reassigns from currentExecutor to newExecutor (or no executor)
if (currentExecutor != address(0)) executorProvidersCount[currentExecutor]--;
executorByProvider[msg.sender] = _newExecutor;
if (_newExecutor != address(0)) executorProvidersCount[_newExecutor]++;
emit LogProviderAssignedExecutor(msg.sender, currentExecutor, _newExecutor);
}
... ...
}
4-3.Gelatoデモ – オートチャージ
Don’t Reinvent the Wheel(タイヤを再発明するな)。
Gelatoのv1のOSS + (Javascript、Solidity)でカスタマイズして、RinkebyでのGYENトークンのオートチャージを試しました。
手順は以下の通りです。
1. External-Providers(0xc4960f4Bb9843e7a512E6F38b9aCEF82B114FdaF)はGelatoに1ETHをデポジットし、Gelatoガスタンクとして、ユーザーに代わってガス代金を支払う。

2. Gelato executorを指定する(デフォルトのexecutorを利用した)

3. ProviderModuleを指定する(ProviderModuleGelatoUserProxyの0x66a35534126B4B0845A2aa03825b95dFaaE88B0Cを利用した)
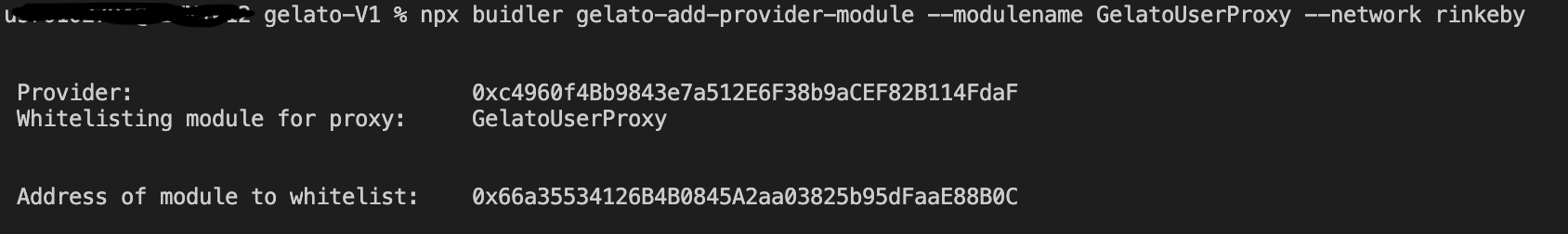
4. Task Specを作成して、ホワイトリストに登録する。
① Conditionコントラクトを作成して、Rinkebyネットワークにデプロイした。
contract ConditionBalanceStateFixful is GelatoStatefulConditionsStandard {
using SafeMath for uint256;
// userProxy => taskReceiptId => refBalance
mapping(address => mapping(address => uint256)) public refBalance;
constructor(IGelatoCore _gelatoCore)
GelatoStatefulConditionsStandard(_gelatoCore)
public
{}
/// @dev use this function to encode the data off-chain for the condition data field
function getConditionData(
address _userProxy,
address _account,
address _token,
bool _greaterElseSmaller
)
public
pure
virtual
returns(bytes memory)
{
return abi.encodeWithSelector(
this.checkRefBalance.selector,
uint256(0), // taskReceiptId placeholder
_userProxy,
_account,
_token,
_greaterElseSmaller
);
}
/// @param _conditionData The encoded data from getConditionData()
function ok(uint256 _taskReceiptId, bytes calldata _conditionData, uint256)
public
view
virtual
override
returns(string memory)
{
(address _userProxy,
address _account,
address _token,
bool _greaterElseSmaller) = abi.decode(
_conditionData[36:], // slice out selector and _taskReceiptId
(address,address,address,bool)
);
return checkRefBalance(
_taskReceiptId, _userProxy, _account, _token, _greaterElseSmaller
);
}
// Specific Implementation
/// @dev Abi encode these parameter inputs. Use a placeholder for _taskReceiptId.
/// @param _taskReceiptId Will be stripped from encoded data and replaced by
/// the value passed in from GelatoCore.
function checkRefBalance(
uint256 _taskReceiptId,
address _userProxy,
address _account,
address _token,
bool _greaterElseSmaller
)
public
view
virtual
returns(string memory)
{
_taskReceiptId;
uint256 _refBalance = refBalance[_userProxy][_account];
// ETH balances
if (_token == 0xEeeeeEeeeEeEeeEeEeEeeEEEeeeeEeeeeeeeEEeE) {
if (_greaterElseSmaller) { // greaterThan
if (_account.balance >= _refBalance) return OK;
return "NotOkETHBalanceIsNotGreaterThanRefBalance";
} else { // smallerThan
if (_account.balance < _refBalance) return OK;
return "NotOkETHBalanceIsNotSmallerThanRefBalance";
}
} else {
// ERC20 balances
IERC20 erc20 = IERC20(_token);
try erc20.balanceOf(_account) returns (uint256 erc20Balance) {
if (_greaterElseSmaller) { // greaterThan
if (erc20Balance >= _refBalance) return OK;
return "NotOkERC20BalanceIsNotGreaterThanRefBalance";
} else { // smallerThan
if (erc20Balance < _refBalance) return OK;
return "NotOkERC20BalanceIsNotSmallerThanRefBalance";
}
} catch {
return "ERC20Error";
}
}
}
function setRefBalance(
address des,
uint256 _balanceDelta
)
external
{
refBalance[msg.sender][des] = _balanceDelta;
}
function getRefBalance(
address userproxy,
address des
)
external
view
returns(uint256)
{
return refBalance[userproxy][des];
}
}
② Actionコントラクトを作成して、Rinkebyネットワークにデプロイした。
contract ActionERC20TransferFromFix is GelatoActionsStandardFull {
function action(
address _user,
IERC20 _sendToken,
address userproxy,
address condition,
address _destination
)
public
virtual
delegatecallOnly("ActionERC20TransferFromFix.action")
{
uint256 fix = ConditionBalanceStateFixful(condition).getRefBalance(userproxy, _destination);
uint256 bal = _sendToken.balanceOf(_destination);
uint256 _sendAmount = 0;
if(bal < fix){
_sendAmount = fix.sub(bal);
_sendToken.safeTransferFrom(
_user, _destination, _sendAmount, "ActionERC20TransferFrom.action:"
);
emit LogOneWay(_user, address(_sendToken), _sendAmount, _destination);
}
}
function termsOk(
uint256, // taskReceipId
address _userProxy,
bytes calldata _actionData,
DataFlow _dataFlow,
uint256, // value
uint256 // cycleId
)
public
view
virtual
override
returns(string memory)
{
_userProxy;
if (this.action.selector != GelatoBytes.calldataSliceSelector(_actionData))
return "ActionERC20TransferFrom: invalid action selector";
if (_dataFlow == DataFlow.In || _dataFlow == DataFlow.InAndOut)
return "ActionERC20TransferFrom: termsOk check invalidated by inbound DataFlow";
(address user, IERC20 sendToken, address userproxy, address condition, address des) = abi.decode(
_actionData[4:],
(address,IERC20,address,address,address)
);
uint256 fix = ConditionBalanceStateFixful(condition).getRefBalance(userproxy, des);
uint256 desb = sendToken.balanceOf(des);
uint256 sendAmount = 0;
if(fix > desb){
sendAmount = fix.sub(desb);
}
try sendToken.balanceOf(user) returns(uint256 sendERC20Balance) {
if (sendERC20Balance < sendAmount)
return "ActionERC20TransferFrom: NotOkUserSendTokenBalance";
} catch {
return "ActionERC20TransferFrom: ErrorBalanceOf";
}
try sendToken.allowance(user, userproxy) returns(uint256 allowance) {
if (allowance < sendAmount)
return "ActionERC20TransferFrom: NotOkUserProxySendTokenAllowance";
} catch {
return "ActionERC20TransferFrom: ErrorAllowance";
}
return OK;
}
}
③ TaskSpecを作成する
const conditionAddress = await run("bre-config", {
deployments: true,
contractname: "ConditionBalanceStateFixful",
});
const actionAddress = await run("bre-config", {
deployments: true,
contractname: "ActionERC20TransferFromFix",
});
const action1 = new Action({
addr: actionAddress,
// no need to include action.data for Task Specs
operation: Operation.Delegatecall, // We are using an action Script here, see smart contract: ActionERC20TransferFrom.sol
dataFlow: DataFlow.None, // Only relevant if this action should return some value to the next, which it not necessary here
termsOkCheck: true, // After the condition is checked, we will also conduct checks on the action contract
value: 0, // Actions that use delegatecall always have value = 0
data: constants.HashZero, // Task Specs dont need data
});
const taskSpec = new TaskSpec({
conditions: [condition.inst], // only need the condition inst address here
actions: [action1], // Actions will be executed from left to right after each other. If one fails, all fail
gasPriceCeil: 0, // Here providers can set the maximum gas price they are willing to pay. Set to 0 to allow any gas price
});
TaskSpecの情報を読み出してみます。
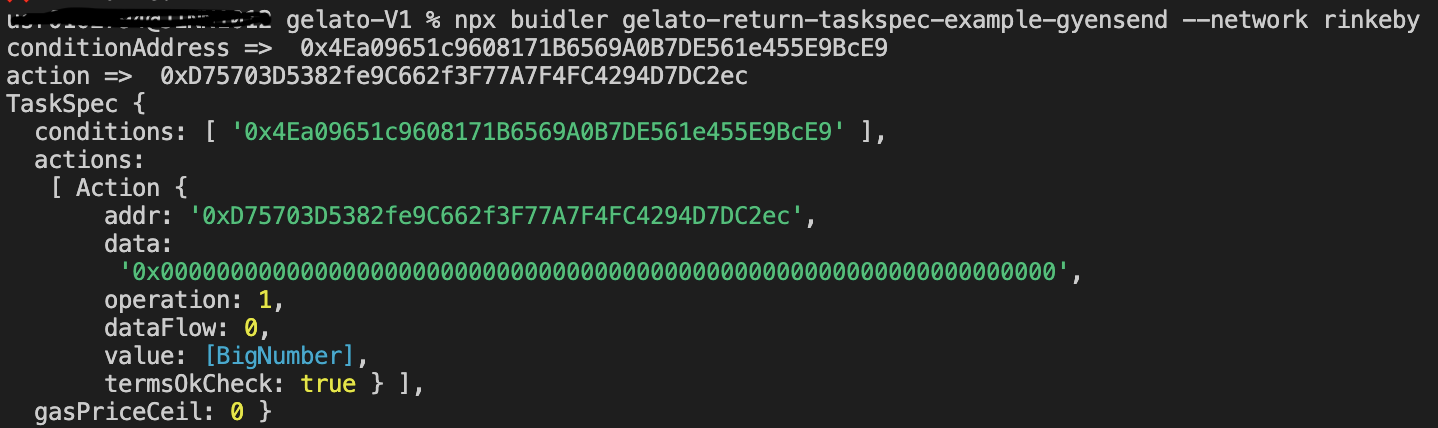
④ TaskSpecをExternal ProviderよりGelatoに追加する。
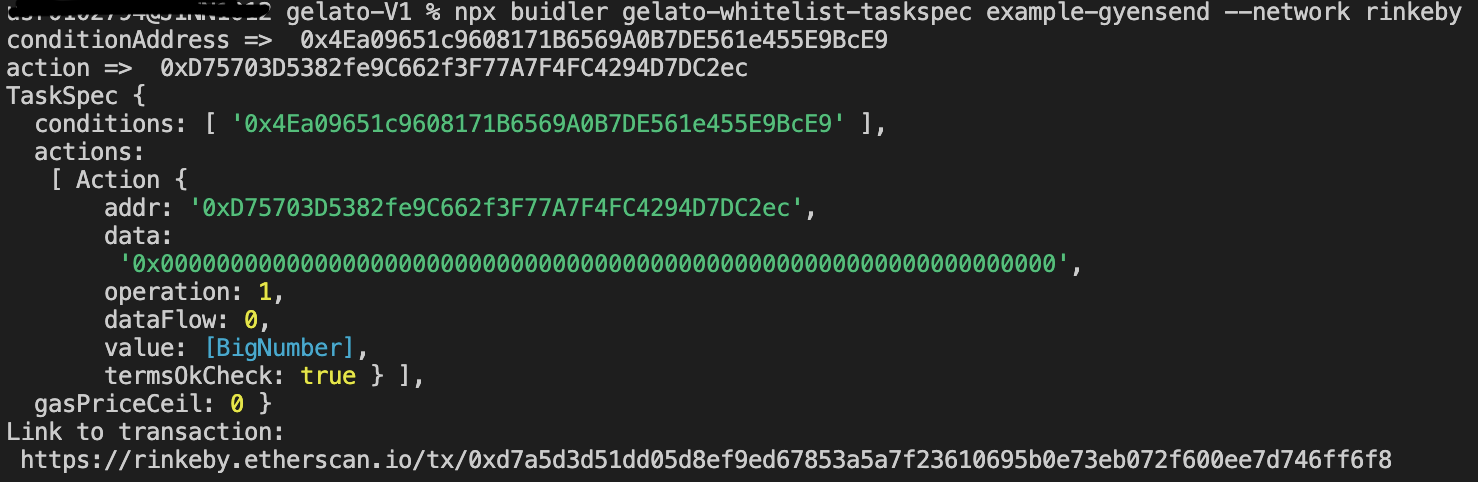
5. 0xE6b48d76Bc4805ABF61F38A55F1D7C362c8BfdA8をブローカーとして、あるアカウントのGYENの閾値をセッティングし、閾値以下となり次第に、閾値までチャージする。
1. ブローカーのプロキシコントラクトをデプロイする。

2. ブローカーはプロキシがブローカーの所持するGYENトークンを引き出せることを許可する。(ブローカーより署名のトランザクション)
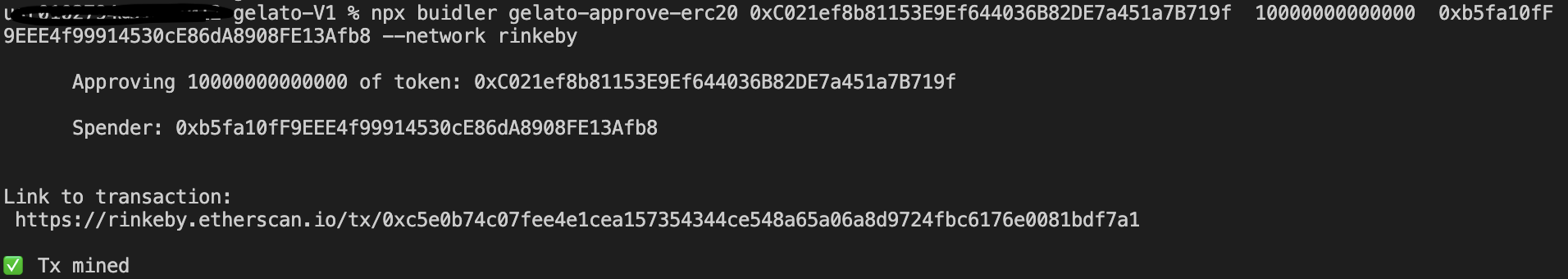
3. ブローカーはアカウント0x833be90d2eCb780cD6ba45a23bcf696397Ad5Fb4の100GYENの閾値のオートチャージをセッティングする。(ブローカーより署名のトランザクション)
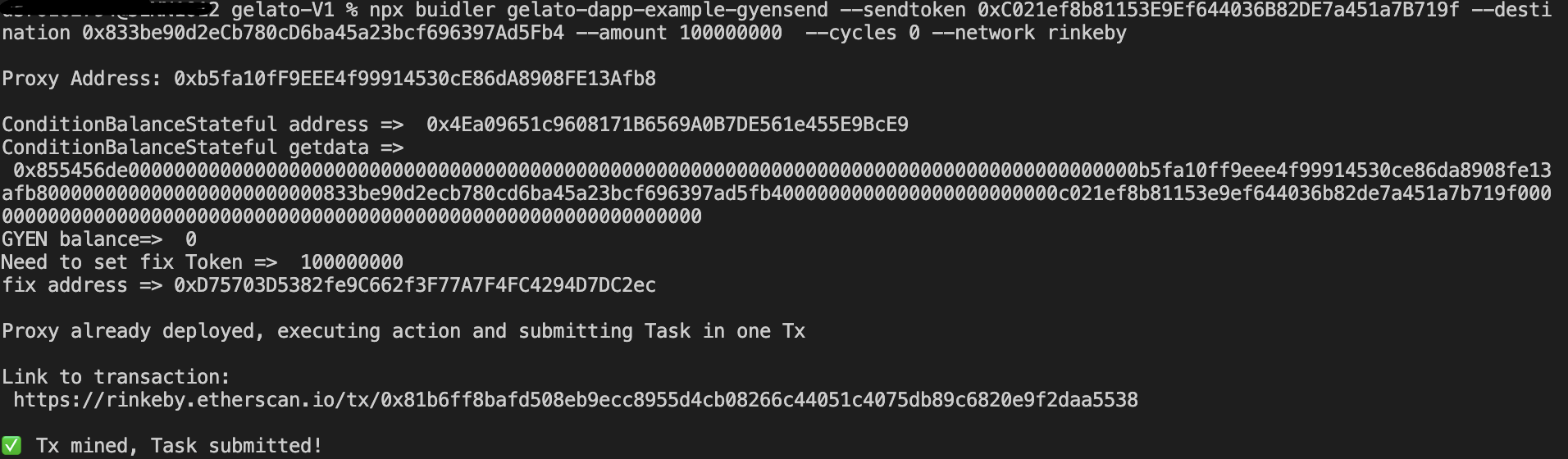
4. ガスレスのwebウォレットで0x833be90d2eCb780cD6ba45a23bcf696397Ad5Fb4でガスレス送金して、オートチャージできるか確認する。
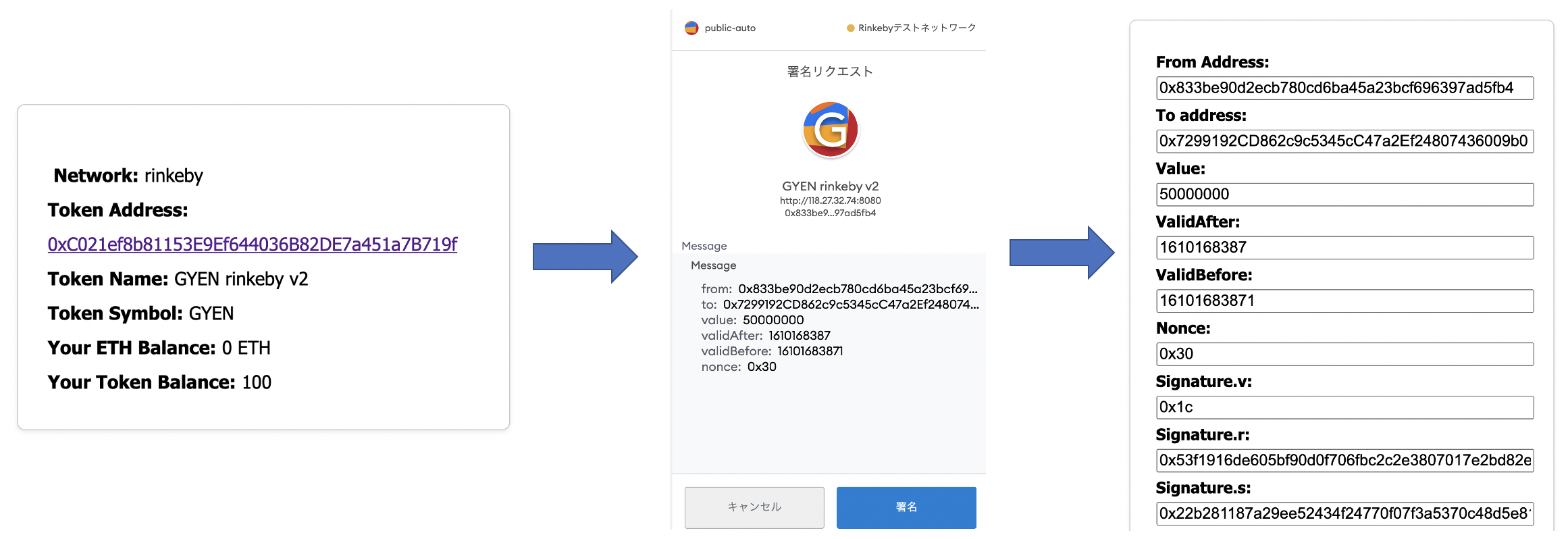
https://rinkeby.etherscan.io/tx/0x0f8f5bf7009d228b4b79c86957e2373c06ce10a09df0e3df4456abdbad370685
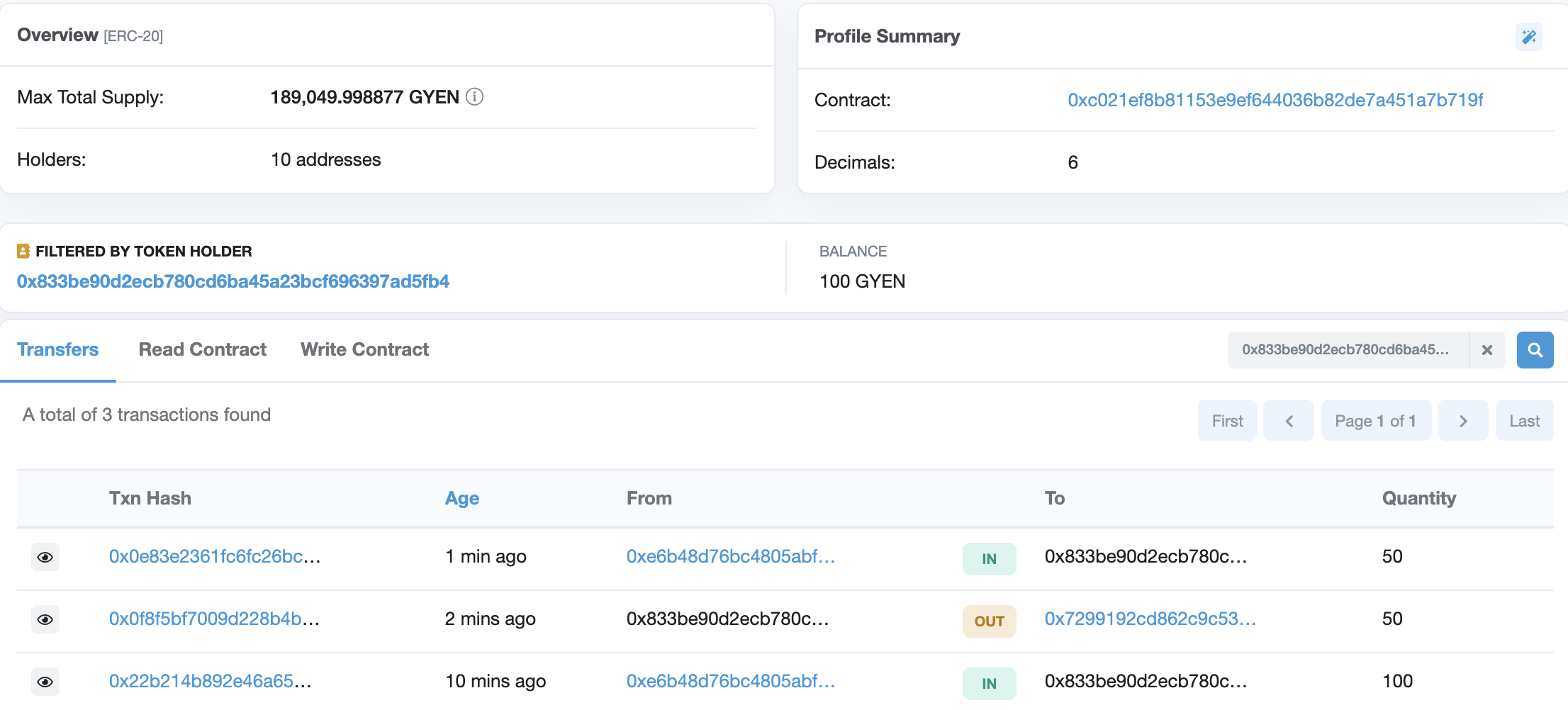
0x833be90d2eCb780cD6ba45a23bcf696397Ad5Fb4のGYENのバランスは100と維持されて、0x833be90d2eCb780cD6ba45a23bcf696397Ad5Fb4へのオートチャージが確認できました。
6. 皆さんも触ってみてください
0x833be90d2eCb780cD6ba45a23bcf696397Ad5Fb4(プライベートキー:0x7b0168217718895a69c66dd7a22085ad999713d1520b38cbb7b9780477c0f690)を自分のMetaMaskウォレットに導入して、ガスレスのwebウォレットでGYENを送金してみてください。
0x833be90d2eCb780cD6ba45a23bcf696397Ad5Fb4のGYENの残高が100GYEN以下となり次第、100GYENまでオートチャージとなるはずです。
5.最後に
今回は前編と後編に分けて、イーサリアムのUX向上の取組の最前線を紹介させていただきましたが、如何でしょうか。
Meta TransactionをあなたのDAPPプロジェクトに統合することで、ユーザーはガスレスで送金、DeFiを楽しめることが可能となることで、UXを向上することに繋がります。
GelatoをあなたのDAPPプロジェクトに統合することで、スマートコントラクトとのやり取りのオートメーションが可能となることで、UXを向上することにも繋がります。
イーサリアムのUXの改善は決して飛躍的ではないですが、正にこの記事のアイキャッチ画像でのストーリーのように、多くの人の乗せる大きい船を作るためには、まずはネズミの乗せるボードで水に浮くかどうか確認し、次は一人の乗せる小さいボートで確認することで、着実に一歩一歩目標に向けますね。
パーミッションレスのDeFiは世界での人々に平等的に金融サービスを享受させるのは決して遠い未来ではないと信じています。
これからのUXの改善に伴い、仮想通貨、DeFiにチャレンジする方々が飛躍的に増えることが大胆に予測します。
(完)
次世代システム研究室では、グループ全体のインテグレーションを支援してくれるアーキテクトを募集しています。アプリケーション開発者の方、次世代システム研究室にご興味を持って頂ける方がいらっしゃいましたら、ぜひ募集職種一覧からご応募をお願いします。
皆さんのご応募をお待ちしています。
グループ研究開発本部の最新情報をTwitterで配信中です。ぜひフォローください。
Follow @GMO_RD





