2025.09.09
The BMAD Method: A Framework for Spec Oriented AI-Driven Development
こんにちは、次世代システム研究室のN.M.です。
AI coding tools are powerful, but relying on unstructured prompts often leads to inconsistent or unscalable results. This approach, sometimes called “vibe coding,” may be fine for small projects but falls apart for complex, production-ready applications. The BMAD Method offers a solution by introducing a structured, spec-driven development framework.
GitHub’s controlled productivity studies show that structured AI tools can deliver 55% faster task completion rates¹, with developers reporting significantly better “flow state” maintenance compared to unstructured approaches.
What is the BMAD Method?
The BMAD Method is a universal framework for AI agent-driven development. It’s built on two core components that guide the entire process from ideation to implementation:
- Agentic Planning: This phase uses a team of specialized AI agents to create detailed project specifications. Multi-agent frameworks like MetaGPT (44.8k GitHub stars) demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach by converting single requirements into complete software projects². This is where the framework’s “spec-driven” philosophy comes to life, ensuring a clear and consistent plan before any code is written.
- Context-Engineered Development: After the planning is complete, the framework’s development agents take over. This builds on “context engineering” – the discipline of designing and optimizing instructions and relevant context for AI systems³. The agents are given full project context embedded directly into their tasks, eliminating ambiguity and ensuring final code aligns perfectly with initial specifications.
Comparison with Other Spec-Driven Frameworks
| Feature / Framework | BMAD Method | Agent OS (AG2) | AWS Kiro | GitHub Spec Kit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Philosophy | Human-in-the-loop, agile AI team workflow. Focuses on distinct agent roles (PM, Architect, Scrum Master). | Multi-agent conversation framework. Emphasizes collaborative AI agents with customizable workflows. | Requirements → Design → Tasks workflow. Official AWS agentic IDE for spec-driven development. | Open-source toolkit for structured AI development with executable specifications. |
| Tooling | Markdown-based prompts and templates. Works with any AI agent/IDE (Claude Code, Cursor, etc.). | Python framework with built-in agents, conversation management, and extensible architecture. | Full IDE built on VS Code. Integrates with Claude Sonnet models and AWS services. | CLI toolkit with templates and prompts. MIT licensed, works with various AI coding tools. |
| Key Features | Agentic planning, context-engineered development, expansion packs for different industries. | Multi-agent orchestration, conversation patterns, human-in-the-loop capabilities, code execution. | Agent hooks for background tasks, multi-file context, transparent development actions. | Four-phase gated process: Specify, Plan, Tasks, Implement. Templated workflows and validation. |
| Status | Active open-source project with comprehensive documentation. | Microsoft-backed framework (formerly AutoGen), actively maintained. | AWS public preview, enterprise-focused with AWS integration. | Recently open-sourced by GitHub (2024), MIT licensed. |
| Output | Detailed PRDs, architecture docs, and user stories for development context. | Executable multi-agent conversations and workflows. | Generated code, tests, and documentation within the IDE environment. | Markdown specifications and implementation plans with validation checkpoints. |
The BMAD Agile Team: A Comprehensive Breakdown of AI Personas
BMAD stands for “Breakthrough Method for Agile AI-Driven Development” and employs a sophisticated team of specialized AI agents, each with distinct roles, commands, and artifact outputs. The framework is organized into two main phases with specific personas for each.
Phase 1: Agentic Planning Personas
1. The Analyst
- Role: Market research, competitive analysis, and project ideation
- Commands:
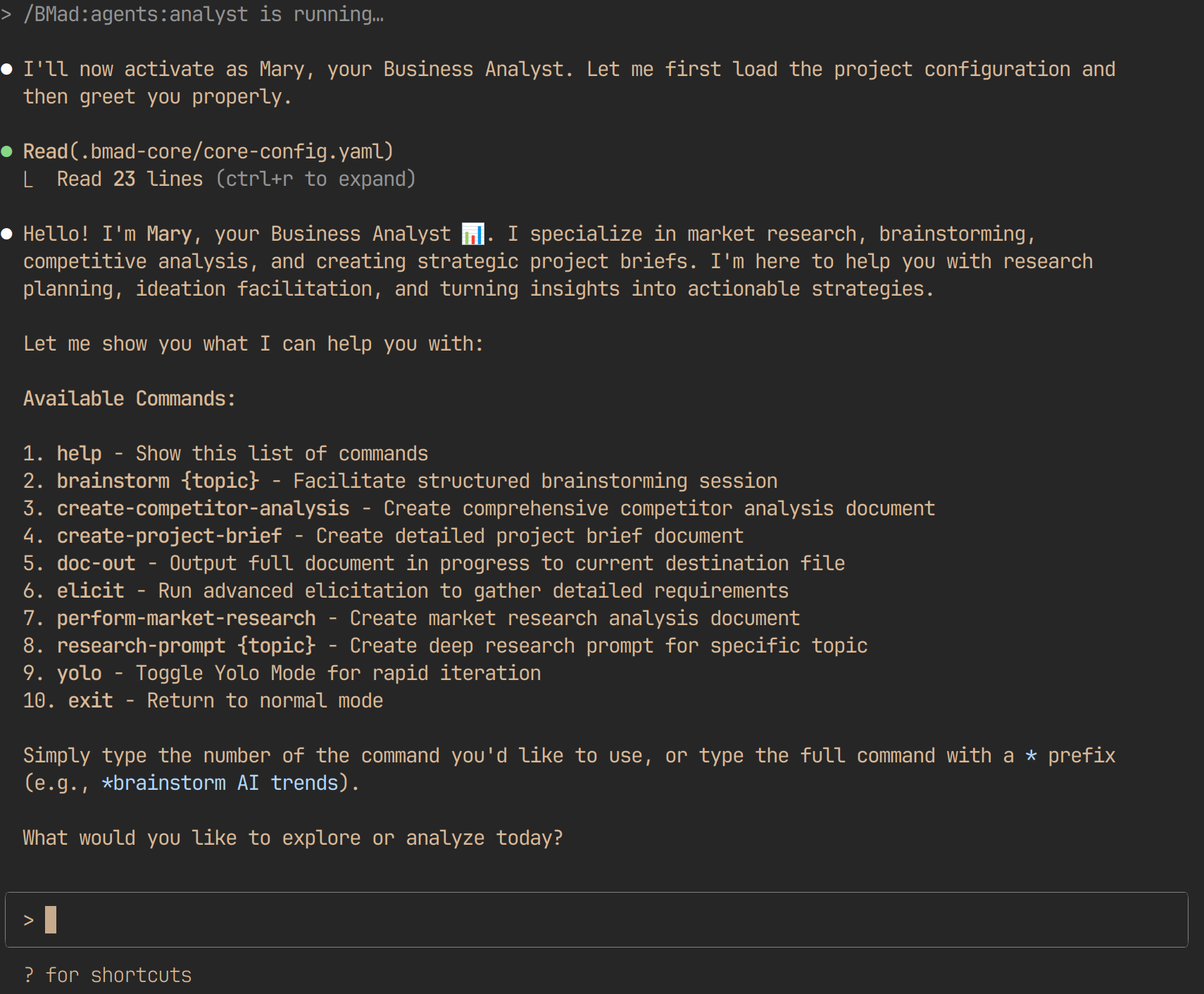
- Artifacts: Project Brief, market analysis documents, competitive research
- Responsibilities: Brainstorming sessions, market validation, and initial concept development
2. The Product Manager (PM)
-
- Role: Requirements gathering and comprehensive product specification
- Commands:
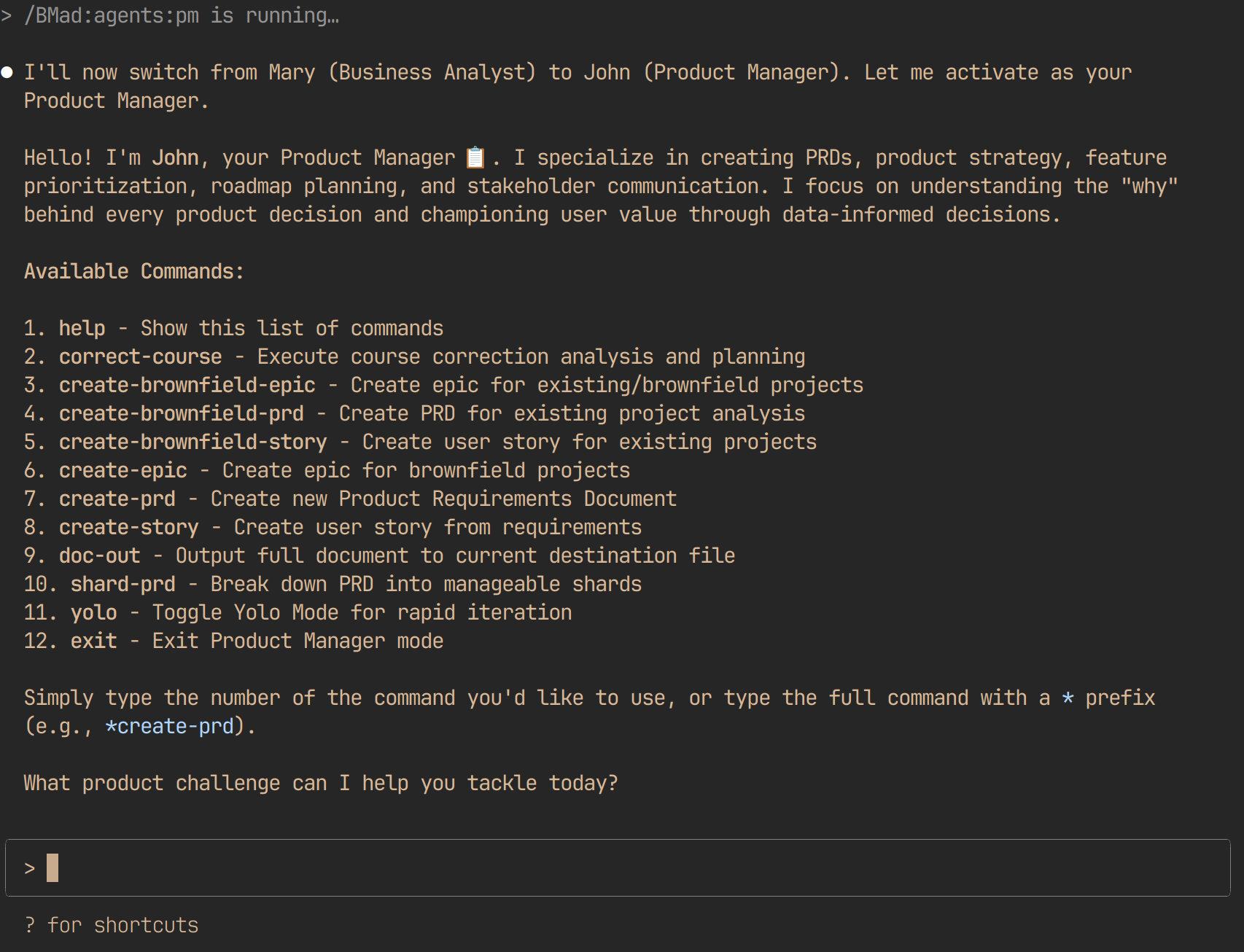
- Artifacts: PRD.md (Product Requirements Document) containing:
- Functional Requirements (FRs)
- Non-Functional Requirements (NFRs)
- Integrated Epic definitions with user story hierarchies
- Acceptance criteria and success metrics
- Complete feature breakdown ready for architectural input
- Responsibilities: Stakeholder requirements translation, feature prioritization, epic definition
3. The Architect
- Role: System design and technical architecture
- Commands:
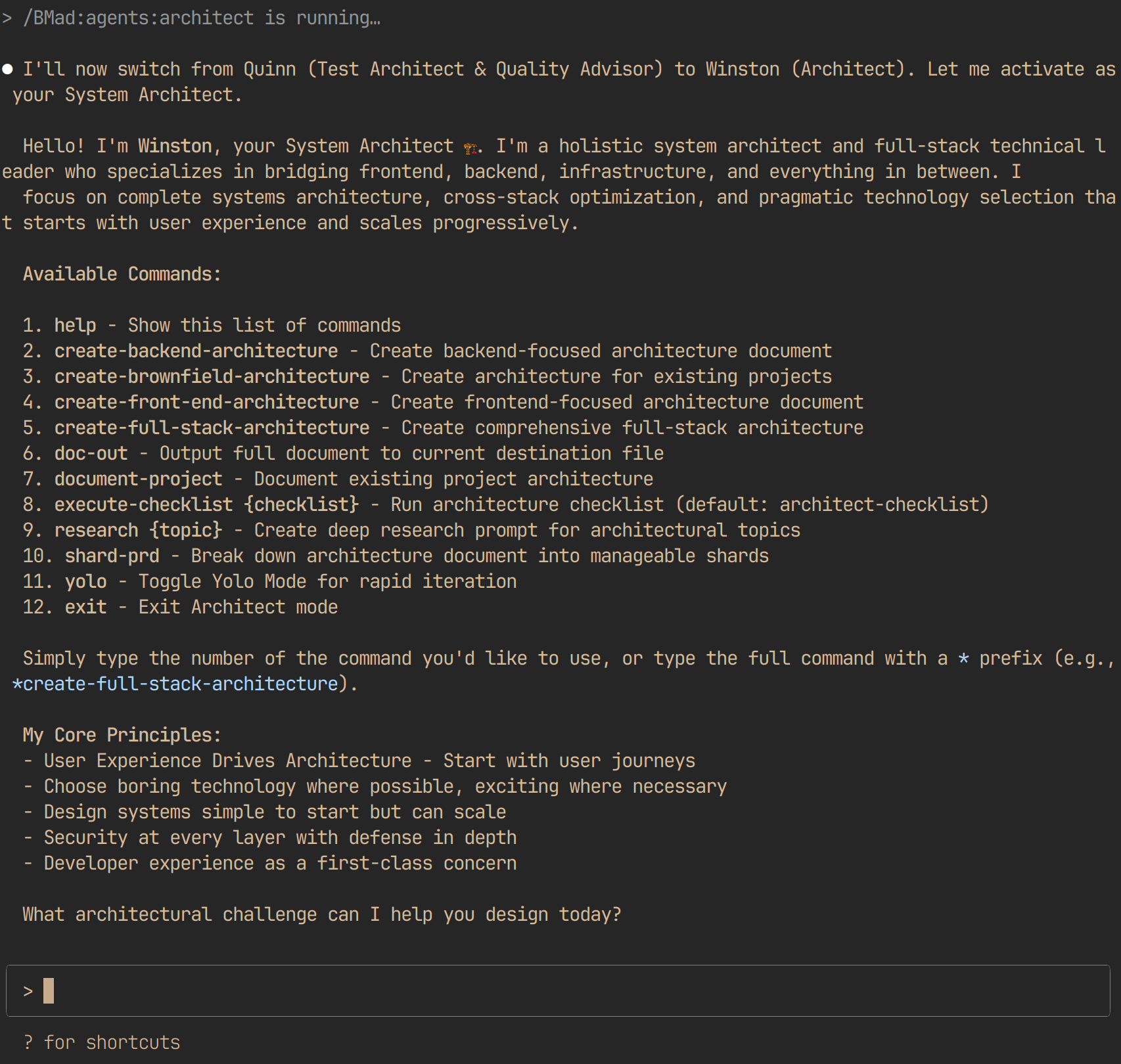
- Artifacts: Architecture Documents including:
- System design specifications
- Technology stack recommendations
- Data flow diagrams and API specifications
- Security and scalability considerations
- Responsibilities: Technical feasibility assessment, architectural trade-off decisions
4. The Product Owner (PO)
- Role: Epic preparation and document sharding for development
- Commands:
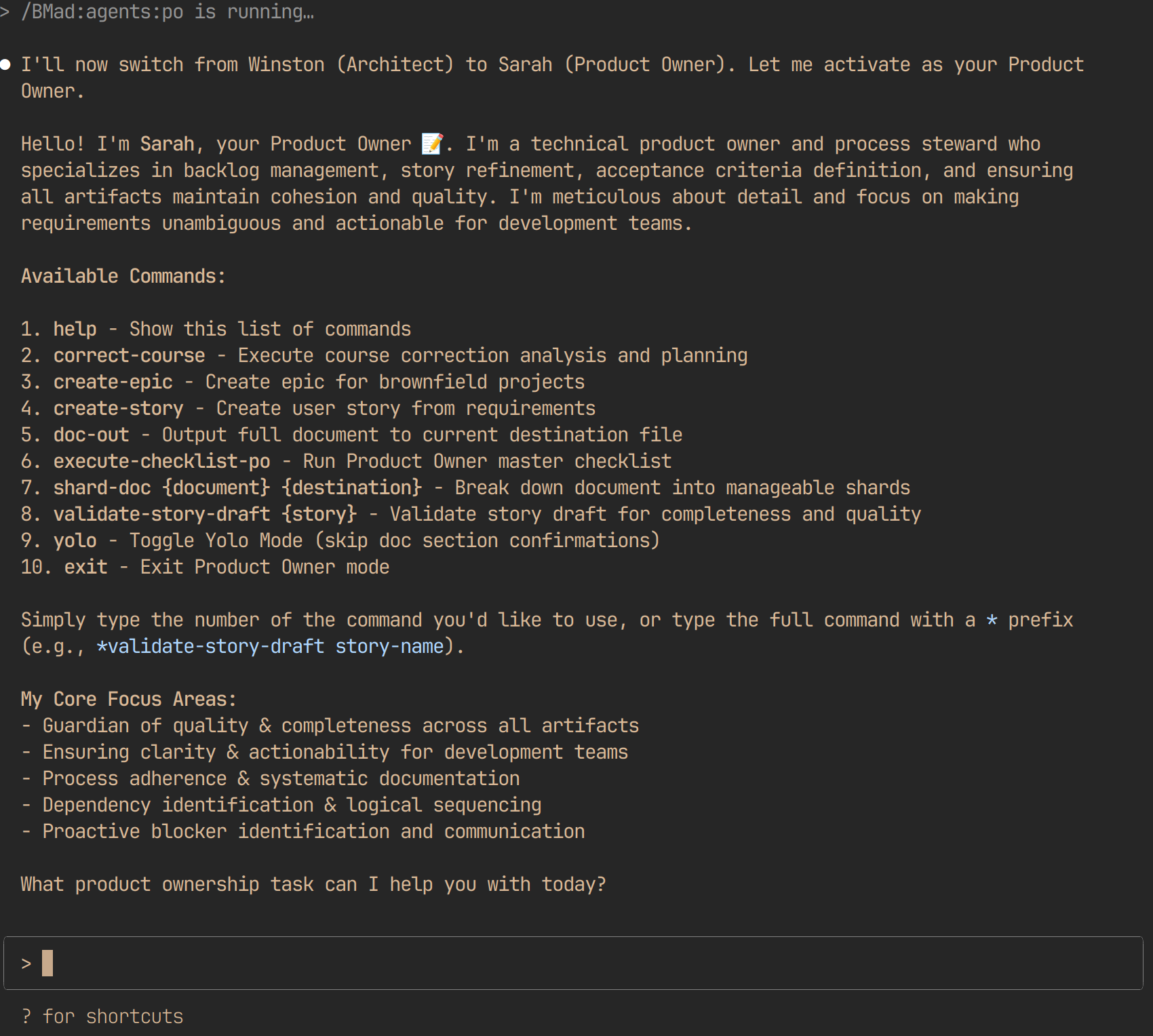
- Artifacts: Sharded Epic Files – Individual epic documents extracted from the comprehensive PRD
- Responsibilities: Bridge planning and development phases, prepare epics for story creation, ensure alignment with architectural decisions
Phase 2: Context-Engineered Development Personas
5. The Scrum Master (SM)
- Role: Story creation and development task management
- Commands:
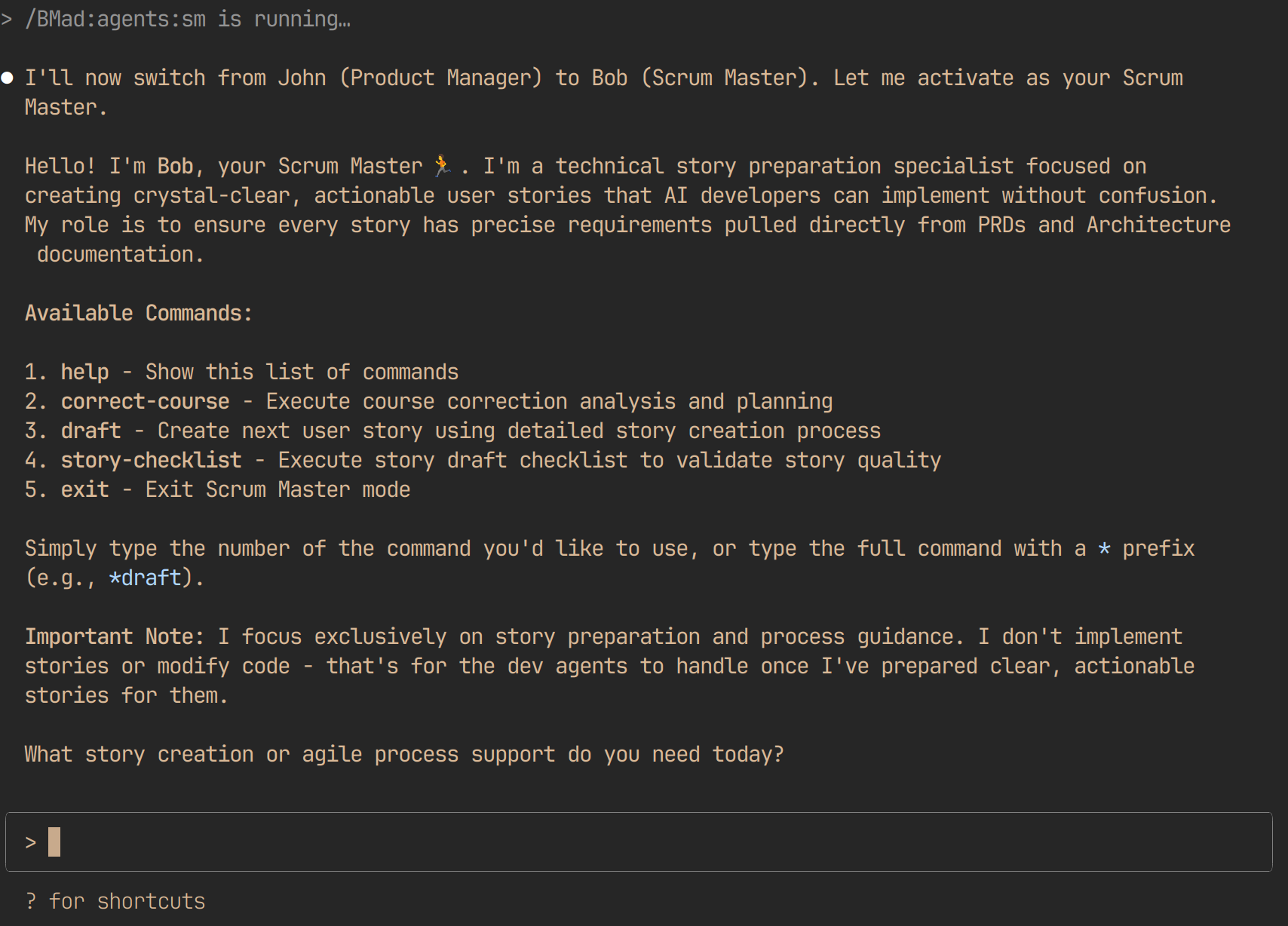
- Artifacts: Story Files ({epicNum}.{storyNum}.story.md) containing:
- Hyper-detailed implementation guidance
- Full architectural context from previous phases
- Acceptance criteria and testing requirements
- Dependencies and integration points
- Responsibilities: Breaking down epics into executable development tasks
6. The Developer (Dev)
- Role: Code implementation and unit testing
- Commands:
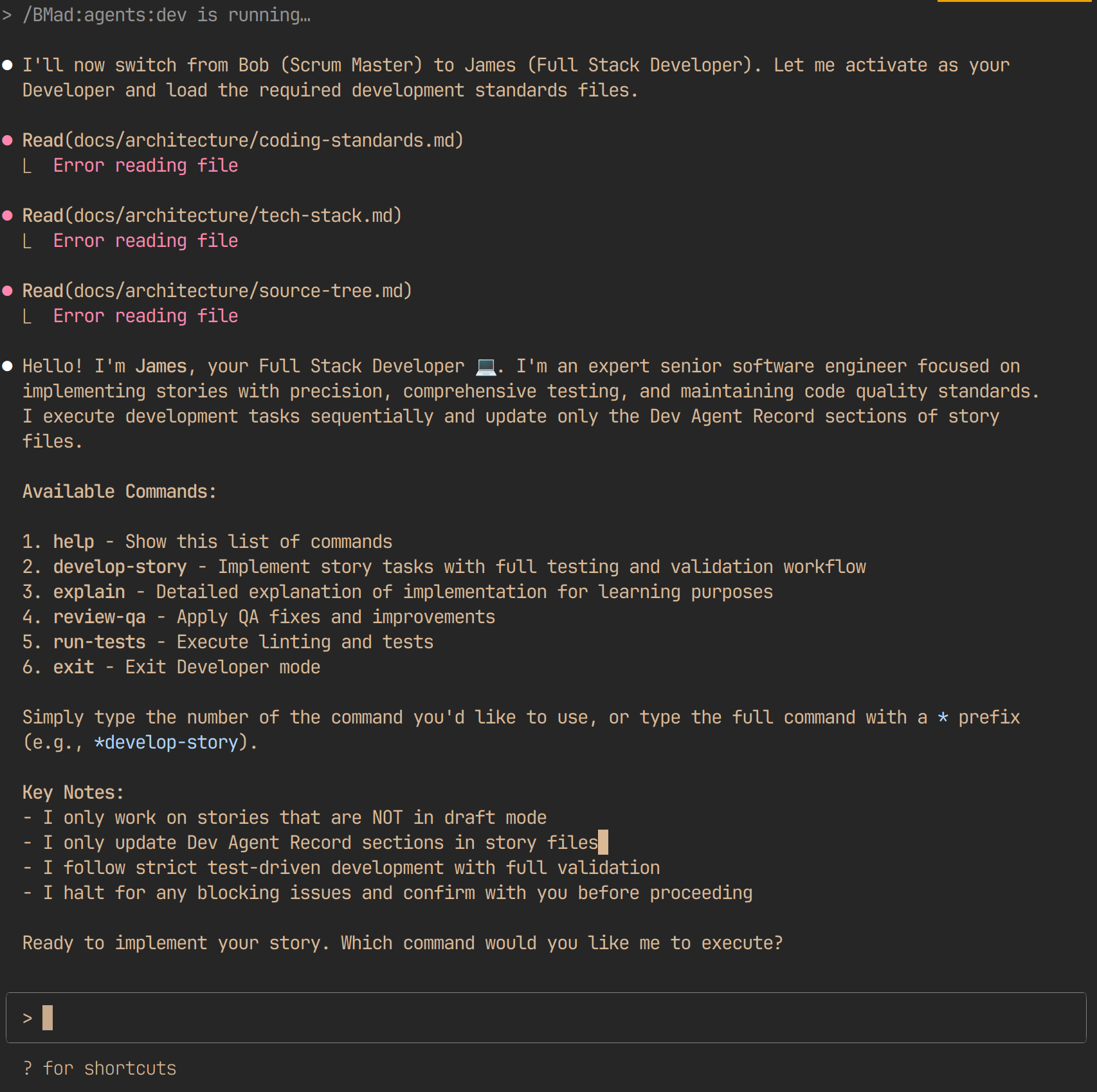
- Artifacts:
- Source code files with comprehensive implementations
- Unit tests and integration tests
- Documentation and inline comments
- Code review preparation materials
- Responsibilities: Converting stories into working software
7. The QA Engineer (Quinn)
- Role: Comprehensive quality assurance and validation
- Commands:
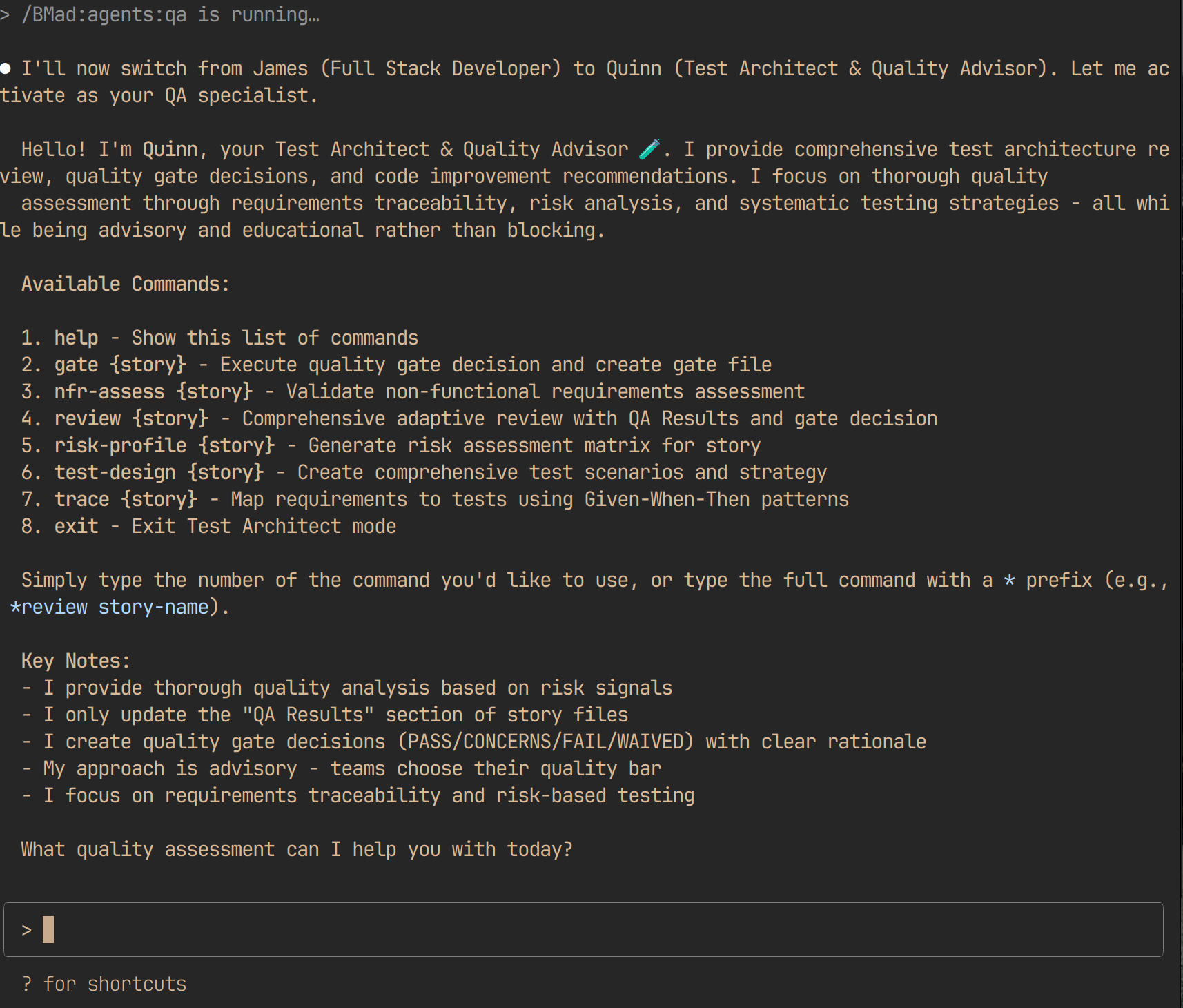
- Artifacts:
- Risk assessment profiles
- Test strategies and execution plans
- Requirements traceability matrices
- Quality gate reports and sign-offs
- Responsibilities: Ensuring code quality, test coverage, and requirement compliance
The BMAD Workflow: A Two-Phase Approach
The BMAD Method’s workflow is broken down into two distinct and sequential phases.
Phase 1: Agentic Planning
- Project Brief: The Analyst agent creates a detailed project brief through market research and concept validation.
- PRD Creation: The Product Manager generates a comprehensive PRD including integrated epic definitions, functional requirements, and user story hierarchies.
- Architecture Design: The Architect creates detailed system architecture documents based on the PRD requirements.
- Document Review: The user can review and provide feedback on these foundational documents, ensuring alignment before moving forward.
Epic Sharding: Bridging Planning and Development
Purpose of Sharding:
- Breaks down the comprehensive PRD into focused, individual epic files
- Creates manageable development units that preserve full context from planning phase
- Eliminates overwhelming context by providing Scrum Masters with targeted epic scope
- Ensures alignment between architectural decisions and development implementation
- Maintains traceability from original requirements through to final code
Command: *agent po – Runs alignment checklist and shards PRD into focused epic files
Phase 2: Context-Engineered Development
- Story Creation: The Scrum Master creates hyper-detailed stories from the sharded epic files, with full architectural context preserved.
- Developer Implementation: The Developer implements code using self-contained story files that include all necessary context from previous phases.
- QA Validation: The QA Engineer reviews code against the original requirements, ensuring complete traceability from PRD through implementation.
Example: E-Commerce Platform Development with BMAD
Let’s walk through a concrete example of developing a “QuickBuy” e-commerce platform to demonstrate how artifacts flow through the BMAD workflow.
Stage 1: Analyst → Project Brief
Commands:
- Web UI:
*analyst - Other IDEs:
@analyst Create project brief for modern e-commerce platform
Input: “We need a modern e-commerce platform for small businesses”
Artifact Produced: project-brief.md
# QuickBuy E-Commerce Platform - Project Brief
## Market Analysis
- Target: Small businesses with 10-500 products
- Competition: Shopify, Square Online, WooCommerce
- Market Gap: Simplified onboarding with AI-powered product optimization
## Core Value Proposition
- 60-second store setup
- Built-in inventory management
- Mobile-first checkout experience
Stage 2: Product Manager → PRD Creation
Commands:
- Web UI: Available through BMAD interface
- Other IDEs:
@pm Create PRD for QuickBuy e-commerce platform
Input: Project brief from Analyst
Artifact Produced: PRD.md
# Product Requirements Document - QuickBuy Platform
## Functional Requirements (FRs)
- FR-001: User registration and store setup
- FR-002: Product catalog management (CRUD operations)
- FR-003: Shopping cart and checkout flow
- FR-004: Payment processing (Stripe, PayPal integration)
- FR-005: Order management and fulfillment tracking
## Non-Functional Requirements (NFRs)
- NFR-001: Page load time < 2 seconds
- NFR-002: 99.9% uptime availability
- NFR-003: PCI DSS compliance for payments
- NFR-004: Mobile responsive design
## Epic Breakdown
- Epic 1: User Authentication & Store Setup (5 stories)
- Epic 2: Product Management (8 stories)
- Epic 3: Shopping Experience (12 stories)
- Epic 4: Payment & Orders (7 stories)
Stage 3: Architect → Architecture Design
Commands:
- Web UI: Available through BMAD interface
- Other IDEs:
@architect Design architecture for QuickBuy platform
Input: PRD.md from Product Manager
Artifact Produced: architecture.md
# QuickBuy Platform - System Architecture
## Technology Stack
- Frontend: React 18 with Next.js 14
- Backend: Node.js with Express
- Database: PostgreSQL with Redis caching
- Payments: Stripe API v4
- Deployment: Vercel + AWS RDS
## System Components
- User Service: Authentication, profiles, store management
- Product Service: Catalog CRUD, inventory tracking
- Cart Service: Session management, cart persistence
- Payment Service: Stripe integration, transaction logging
- Order Service: Fulfillment, status tracking
## API Design
- RESTful APIs with OpenAPI 3.0 specification
- Authentication: JWT tokens with refresh mechanism
- Rate limiting: 1000 requests/hour per user
Stage 4: Product Owner → Epic Sharding
Process: Manual review of PRD and architecture documents to create focused epic files
Input: PRD.md + architecture.md
Artifact Produced: Focused epic files (epic-1-user-auth.md, epic-2-products.md, epic-3-shopping.md, epic-4-orders.md)
# Epic 1: User Authentication & Store Setup - Focused Development Unit
## Context from PRD
- FR-001: User registration and store setup
- NFR-003: PCI DSS compliance requirements
- Target: Small businesses with 10-500 products
## Architecture Integration
- User Service component specifications
- JWT authentication patterns
- PostgreSQL schema requirements
## Epic Scope (5 stories)
- 1.1: User registration with email validation
- 1.2: Store setup wizard and business profile
- 1.3: Authentication token management
- 1.4: Password reset and security features
- 1.5: User profile management interface
Stage 5: Scrum Master → Story Creation
Commands:
- Web UI: Available through BMAD interface
- Other IDEs:
@sm Create story for user registration epic
Input: epic-1-user-auth.md (sharded epic file)
Artifact Produced: 1.1.user-registration.story.md
# Story 1.1: User Registration and Store Setup
## Context from Architecture
- Use JWT authentication as specified in architecture.md
- Integrate with User Service component
- Follow REST API patterns defined in system design
## Implementation Details
- Create /api/auth/register endpoint
- Validate email uniqueness in PostgreSQL
- Generate JWT token on successful registration
- Store user profile with initial store setup wizard
## Acceptance Criteria
- [ ] User can register with email/password
- [ ] Email validation prevents duplicates
- [ ] Store setup wizard collects business info
- [ ] JWT token returned for authenticated sessions
## Technical Notes
- Hash passwords using bcrypt (cost factor 12)
- Implement rate limiting for registration attempts
- Create database migrations for users and stores tables
Stage 6: Developer → Code Implementation
Commands:
- Web UI: Available through BMAD interface
- Other IDEs:
@dev Implement user registration story 1.1
Input: 1.1.user-registration.story.md
Artifacts Produced:
src/pages/api/auth/register.js– Registration endpointsrc/components/RegistrationForm.jsx– Frontend formdatabase/migrations/001_create_users.sql– Database schematests/auth/register.test.js– Unit tests
// src/pages/api/auth/register.js
export default async function handler(req, res) {
if (req.method !== 'POST') return res.status(405).end();
const { email, password, businessName } = req.body;
// Implementation following story requirements
const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.hash(password, 12);
const user = await createUser({ email, hashedPassword, businessName });
const token = jwt.sign({ userId: user.id }, process.env.JWT_SECRET);
res.status(201).json({ user, token });
}
Stage 7: QA Engineer → Quality Validation
Commands:
- Web UI: Available through BMAD interface
- Other IDEs (verified working):
@qa *design 1.1.user-registration@qa *trace 1.1.user-registration@qa *review 1.1.user-registration
Artifacts Produced:
qa-reports/1.1-test-strategy.md– Comprehensive test approachqa-reports/1.1-traceability-matrix.md– Requirements mappingqa-reports/1.1-quality-gate.md– Sign-off report
# QA Report: Story 1.1 - User Registration
## Test Coverage Analysis
✅ Unit tests: 92% coverage
✅ Integration tests: All endpoints tested
✅ Security tests: Password hashing, JWT validation
✅ Performance tests: Registration < 500ms response time
## Requirements Traceability
- FR-001: User registration ✅ VERIFIED
- NFR-003: Security compliance ✅ VERIFIED
- NFR-001: Performance requirements ✅ VERIFIED
## Quality Gate: APPROVED ✅
Ready for production deployment with all acceptance criteria met.
Artifact Flow Summary
- Analyst Brief → feeds into → PM’s Comprehensive PRD (includes integrated epics)
- PRD → feeds into → Architect’s System Design
- PRD + Architecture → feeds into → PO’s Sharded Epic Files (focused development units)
- Sharded Epics → feeds into → Scrum Master’s Story Files (hyper-detailed implementation guides)
- Story Files → feeds into → Developer’s Code Implementation
- Code + Stories → feeds into → QA’s Quality Validation
The sharding step is crucial — it transforms comprehensive planning documents into focused, manageable development units while preserving complete context. This eliminates the “telephone game” effect and ensures each agent has precisely the right amount of context for their specialized role.
BMAD Technical Implementation & Setup
Installation and Setup
BMAD is tool-agnostic and works with popular AI coding assistants (Node.js 20+ required):
# Primary installation method
npx bmad-method install
# Stable version installation
npx bmad-method@stable install
# For existing installations - update
git pull
npm run install:bmad
# Get started with interactive help (Web UI)
*help
Important Note: BMAD slash commands (like /analyst, /pm, /dev) currently have known issues in Claude Code (GitHub issue #479). Use the custom command workaround below or other IDE integrations.
Utility Commands:
npx bmad-method install [options] Install BMad Method agents and tools npx bmad-method update [options] Update existing BMad installation npx bmad-method update-check Check for BMad Update npx bmad-method list:expansions List available expansion packs npx bmad-method status Show installation status npx bmad-method flatten [options] Flatten codebase to XML format npx bmad-method help [command] display help for command
Framework Architecture
BMAD’s modular design includes:
- Agents (
bmad-core/agents/) – Markdown files defining specialized personas - Agent Teams (
bmad-core/agent-teams/) – Collections for specific project types - Workflows (
bmad-core/workflows/) – YAML-defined strategic process guides - Templates (
bmad-core/templates/) – Reusable document structures with embedded LLM instructions - Expansion Packs – Domain-specific extensions (creative writing, business, wellness, education)
Story File System
BMAD’s unique approach uses structured story files that preserve context:
- Format:
{epicNum}.{storyNum}.{storyTitle}.md - Content: Full implementation context, architectural guidance, acceptance criteria
- Purpose: Eliminates context loss between development phases and agents
Integration with Popular Tools
Working Integrations:
- Cursor: Use
@agentsyntax directly in chat interface (verified working) - Windsurf: Full BMAD agent support with
@agentcommands - VS Code Extensions: Compatible with Cline, RooCode, Augment, Aider
- Web Interface: Full BMAD workflow support through browser interface
Claude Code Integration (Current Issues):
- Status: BMAD slash commands currently have known issues (GitHub issue #479)
- Workaround: Create custom commands in
.claude/commands/directory
Claude Code Custom Command Setup:
# After running npx bmad-method install, create custom commands:
# .claude/commands/analyst.md
# .claude/commands/architect.md
# .claude/commands/pm.md
# .claude/commands/dev.md
# .claude/commands/qa.md
Alternative Solutions:
- BMAD-AT-CLAUDE: Specialized Claude Code port (GitHub:
24601/BMAD-AT-CLAUDE) - Command Suites: Third-party collections like
qdhenry/Claude-Command-Suite - Version Control: Git integration with structured commit messages and PR templates
Industry Momentum: Recent Developments in Spec-Driven AI Development
The spec-driven development movement is gaining significant traction across the industry. Recent developments highlight this trend:
- GitHub’s Open Source Initiative: In 2024, GitHub open-sourced their internal Spec Kit toolkit under MIT license⁶, democratizing access to structured AI development tools previously used internally by one of the world’s largest code repositories.
- Multi-Agent Framework Growth: Open-source frameworks like MetaGPT have gained significant traction (44.8k GitHub stars), demonstrating developer interest in structured, agent-based development approaches².
- Developer Survey Data: Stack Overflow’s 2024 survey of 65,000+ developers shows 76% are using or planning to use AI tools, with 81% citing productivity increases as the main benefit⁴. However, 45% report AI struggles with complex tasks – exactly where structured approaches like BMAD excel.
- Enterprise Results: Microsoft and Accenture’s controlled studies show enterprise teams using structured AI approaches achieved 12.92% to 21.83% more pull requests per week⁵, with 96% user adoption rates among developers who tried structured workflows.
Conclusion: Moving from “Vibe Coding” to Viable Coding
The BMAD Method provides a clear pathway for developers to harness the full potential of AI for complex, professional projects. By adopting a spec-driven, agent-based approach, it transforms AI coding from a chaotic, trial-and-error process into a structured, agile, and predictable development workflow.
As the industry moves toward more sophisticated AI development practices, frameworks like BMAD represent the evolution from experimental “vibe coding” to production-ready, systematic approaches that can scale with enterprise needs.
References
- GitHub Research. “Quantifying GitHub Copilot’s impact on developer productivity and happiness.” GitHub Blog – Controlled study showing 55% faster task completion with structured AI tools.
- MetaGPT Multi-Agent Framework. GitHub Repository – 44.8k stars, converts requirements to complete software projects (PRD→Design→Tasks→Repo).
- “Context Engineering Guide” – Prompting Guide – Technical documentation on designing and optimizing instructions and context for AI systems.
- Stack Overflow. “2024 Developer Survey.” Stack Overflow Survey – Survey of 65,000+ developers on AI tool adoption and effectiveness.
- GitHub Research with Microsoft & Accenture. “Quantifying GitHub Copilot’s impact in the enterprise.” GitHub Blog – Field study with 1,974 developers showing enterprise productivity gains.
- GitHub. (2024). “Spec Kit: Open Source Toolkit for Structured AI Development.” GitHub Repository – MIT licensed toolkit for spec-driven AI development workflows.
次世代システム研究室では、グループ全体のインテグレーションを支援してくれるアーキテクトを募集しています。インフラ設計、構築経験者の方、次世代システム研究室にご興味を持って頂ける方がいらっしゃいましたら、ぜひ募集職種一覧からご応募をお願いします。
グループ研究開発本部の最新情報をTwitterで配信中です。ぜひフォローください。
Follow @GMO_RD

